Intro
Discover the ins and outs of US Marines pay with our comprehensive guide. Learn about base pay, allowances, and special pays, as well as rank-based salaries and promotions. Understand how military pay scales work and what benefits Marines receive, from Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH) to special duty pay.
Serving in the United States Marine Corps is a noble and challenging profession that requires sacrifice, dedication, and hard work. One of the most important aspects of being a Marine is understanding the compensation and benefits that come with the job. In this article, we will delve into the world of US Marines pay, highlighting five essential things you need to know.
The Marine Corps offers a competitive salary and benefits package to its members, which can vary depending on factors such as rank, time in service, and job specialty. Whether you're a new recruit or a seasoned veteran, it's essential to understand the ins and outs of Marines pay to make informed decisions about your career and financial future.
1. Basic Pay: The Foundation of Marines Pay
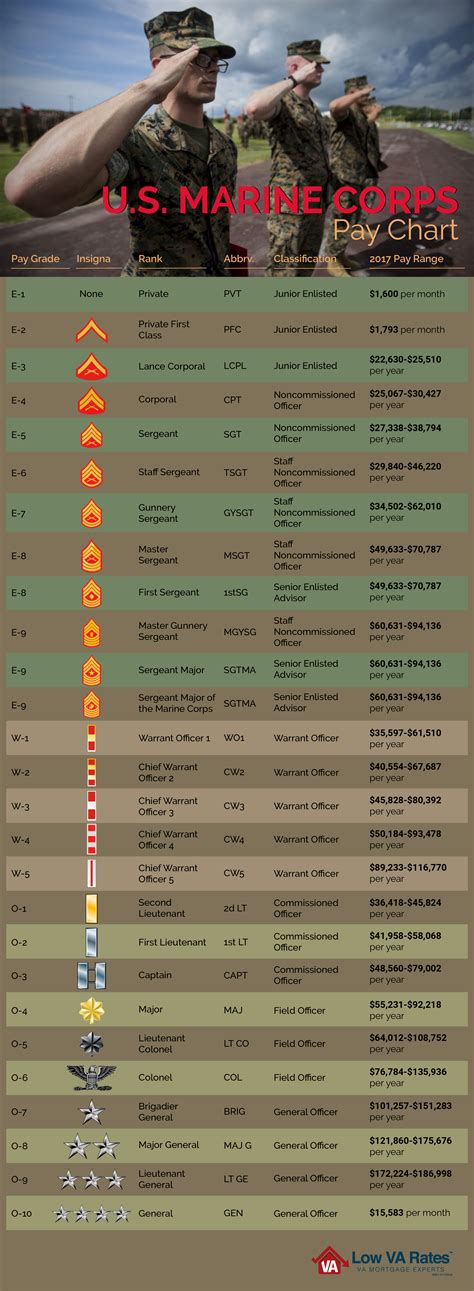
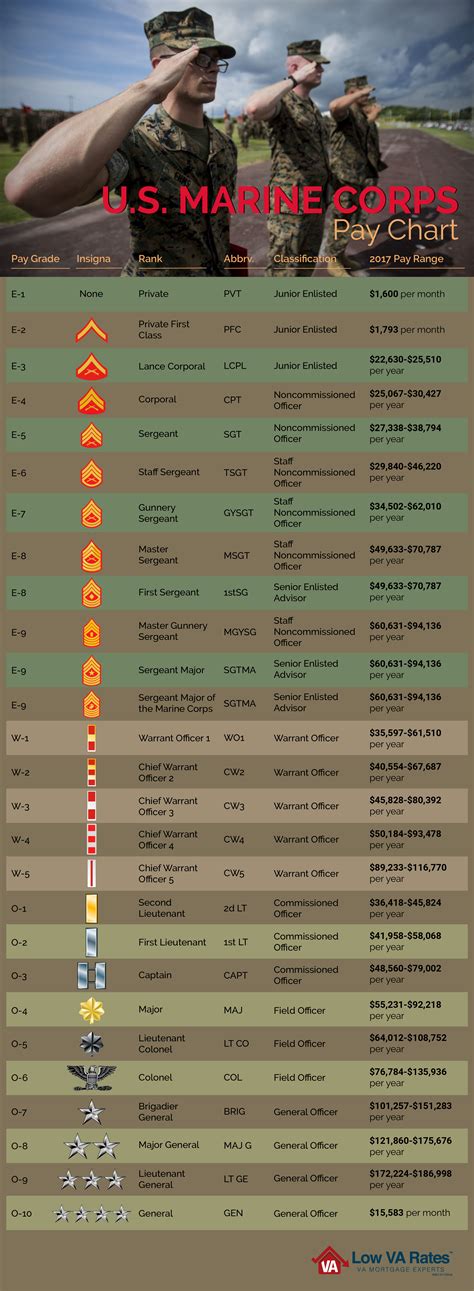
Basic pay is the foundation of a Marine's compensation package, and it's based on the member's rank and time in service. The Marine Corps uses a pay grade system, which consists of nine enlisted pay grades (E-1 to E-9) and eleven officer pay grades (O-1 to O-10). As Marines advance in rank and gain more experience, their basic pay increases accordingly.
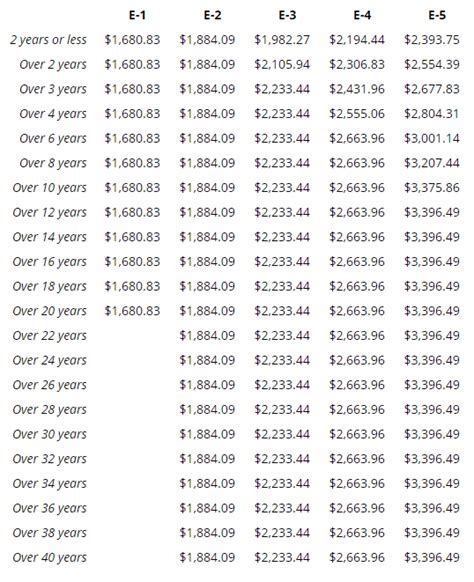
For example, a Private First Class (E-2) with less than two years of service can expect to earn around $1,942 per month in basic pay, while a Sergeant Major (E-9) with over 20 years of service can earn up to $5,173 per month.
How Basic Pay Works
Basic pay is calculated based on the member's pay grade and time in service. Marines receive a pay raise every year, and their basic pay can also increase when they advance in rank or gain more experience.
Here's a breakdown of the 2022 basic pay rates for enlisted Marines:
- Private (E-1): $1,733 per month
- Private First Class (E-2): $1,942 per month
- Lance Corporal (E-3): $2,043 per month
- Corporal (E-4): $2,343 per month
- Sergeant (E-5): $2,533 per month
- Staff Sergeant (E-6): $2,833 per month
- Gunnery Sergeant (E-7): $3,233 per month
- Master Sergeant (E-8): $3,633 per month
- Sergeant Major (E-9): $4,033 per month
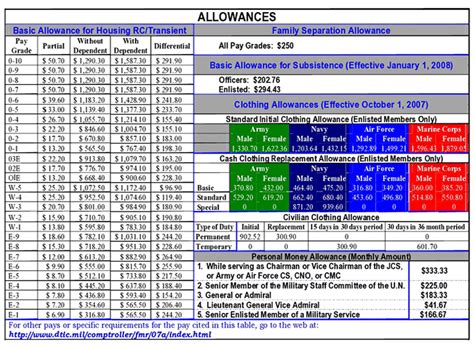
2. Allowances: Supplementing Basic Pay
In addition to basic pay, Marines receive various allowances to help cover the costs of living, housing, and food. These allowances can vary depending on the member's location, rank, and family size.
Some common allowances include:
- Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH): This allowance helps cover the costs of housing, whether Marines are living on or off base.
- Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS): This allowance helps cover the costs of food, whether Marines are eating at a base dining facility or buying their own groceries.
- Cost of Living Allowance (COLA): This allowance helps cover the costs of living in areas with a high cost of living.
How Allowances Work
Allowances are calculated based on the member's location, rank, and family size. Marines receive a monthly allowance, which is added to their basic pay.
Here's an example of how allowances can impact a Marine's total compensation:
- A Private First Class (E-2) with a family of four, living on base, might receive a monthly BAH of $1,200, a BAS of $369, and a COLA of $500.
- A Staff Sergeant (E-6) with a family of two, living off base, might receive a monthly BAH of $1,800, a BAS of $369, and a COLA of $0.
3. Bonuses: Additional Incentives
The Marine Corps offers various bonuses to incentivize Marines to serve in specific roles, complete challenging training programs, or reenlist.

Some common bonuses include:
- Enlistment Bonus: New recruits can earn a bonus of up to $40,000 for enlisting in the Marine Corps.
- Reenlistment Bonus: Marines who reenlist can earn a bonus of up to $90,000.
- Specialty Bonus: Marines who serve in high-demand specialties, such as aviation or cybersecurity, can earn a bonus of up to $50,000.
How Bonuses Work
Bonuses are offered to incentivize Marines to serve in specific roles or complete challenging training programs. Marines can earn multiple bonuses throughout their career, which can significantly impact their total compensation.
Here's an example of how bonuses can impact a Marine's total compensation:
- A Private First Class (E-2) who enlists in the Marine Corps and completes boot camp might earn a $10,000 enlistment bonus.
- A Staff Sergeant (E-6) who reenlists for another six years might earn a $30,000 reenlistment bonus.
4. Benefits: Comprehensive Support
The Marine Corps offers a comprehensive benefits package to support Marines and their families. These benefits include:
- Health Insurance: Marines and their families have access to comprehensive health insurance, including medical, dental, and pharmacy benefits.
- Education Benefits: Marines can earn education benefits, including the Montgomery GI Bill and the Marine Corps Tuition Assistance Program.
- Retirement Benefits: Marines who serve for 20 years or more can earn a pension and access to retirement benefits.

How Benefits Work
Benefits are offered to support Marines and their families. Marines can access these benefits throughout their career and after they retire.
Here's an example of how benefits can impact a Marine's total compensation:
- A Private First Class (E-2) who earns a bachelor's degree using the Marine Corps Tuition Assistance Program might save up to $10,000 in education expenses.
- A Staff Sergeant (E-6) who retires after 20 years might earn a pension of up to $3,000 per month.
5. Taxes: Understanding the Impact
Marines pay federal income taxes on their basic pay, allowances, and bonuses. However, they do not pay taxes on certain benefits, such as health insurance and education benefits.

How Taxes Work
Taxes are calculated based on the member's basic pay, allowances, and bonuses. Marines can file taxes annually and claim deductions for certain benefits.
Here's an example of how taxes can impact a Marine's total compensation:
- A Private First Class (E-2) who earns $30,000 per year might pay around $4,000 in federal income taxes.
- A Staff Sergeant (E-6) who earns $60,000 per year might pay around $8,000 in federal income taxes.
Gallery of US Marines Pay
US Marines Pay Image Gallery







Frequently Asked Questions
How much do Marines get paid?
+Marines pay varies based on rank, time in service, and job specialty. Basic pay ranges from $1,733 per month for a Private (E-1) to $5,173 per month for a Sergeant Major (E-9).
What allowances do Marines receive?
+Marines receive various allowances, including Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH), Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS), and Cost of Living Allowance (COLA).
What benefits do Marines receive?
+Marines receive comprehensive benefits, including health insurance, education benefits, and retirement benefits.
In conclusion, US Marines pay is a complex system that includes basic pay, allowances, bonuses, and benefits. Understanding these components can help Marines make informed decisions about their career and financial future. By taking advantage of the various incentives and benefits offered by the Marine Corps, Marines can earn a competitive salary and build a secure financial future.
