Intro
Discover the ins and outs of mandatory army service, a requirement for many countries every 4 years. Learn about the history, benefits, and implications of compulsory military service, including draft systems, conscientious objector rights, and its impact on young adults, national security, and global politics.
Every four years, millions of young adults around the world receive a letter that will change their lives forever. It's not a congratulatory message or a birthday greeting, but a notice to report for mandatory military service. For many, this is a rite of passage, a chance to serve their country, and a stepping stone to adulthood. But what exactly is mandatory army service, and how does it work?
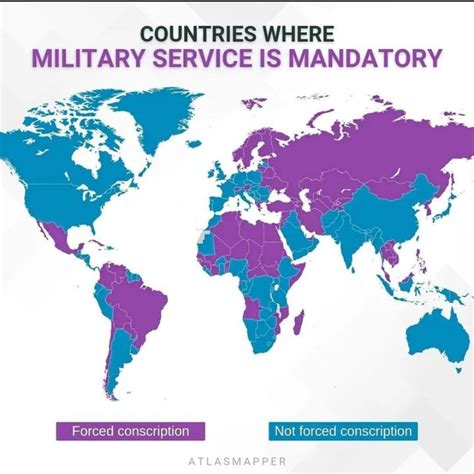
Mandatory army service, also known as national service or conscription, is a system where citizens are required to serve in the military for a certain period. This system is practiced in over 60 countries worldwide, including Israel, South Korea, and Greece. The length of service varies from country to country, but it typically ranges from 1 to 3 years.

History of Mandatory Army Service
The concept of mandatory army service dates back to ancient times. In ancient Greece and Rome, citizens were required to serve in the military to defend their city-states. This system was also used in other civilizations, including the Ottoman Empire and Napoleon's France. However, it wasn't until the 20th century that mandatory army service became widespread.
After World War II, many countries implemented mandatory army service as a way to rebuild their militaries and maintain national security. The Soviet Union, for example, had a mandatory service system that lasted for 2 years. Other countries, like Israel and South Korea, also adopted this system to defend against neighboring threats.
Benefits of Mandatory Army Service
Proponents of mandatory army service argue that it has numerous benefits, both for the individual and society as a whole. Some of these benefits include:
- National security: Mandatory army service ensures that a country has a large and capable military to defend against external threats.
- Discipline and skills: Military training teaches valuable skills like discipline, teamwork, and leadership, which can benefit individuals throughout their lives.
- Civic engagement: Mandatory army service can foster a sense of patriotism and civic engagement, as citizens work together to defend their country.
- Education and training: Many militaries offer education and training programs that can help individuals develop new skills and pursue higher education.
How Mandatory Army Service Works
The process of mandatory army service varies from country to country, but most systems follow a similar pattern:
- Registration: Citizens are required to register for military service at a certain age, usually between 18 and 25.
- Draft: A random selection process, known as a draft, is used to choose citizens for military service.
- Training: Selected citizens undergo military training, which can last from several months to several years.
- Service: After training, citizens are assigned to a military unit and serve for a certain period, usually 1 to 3 years.
Challenges and Controversies
While mandatory army service has its benefits, it also faces several challenges and controversies. Some of these include:
- Conscientious objection: Some citizens may object to military service on moral or religious grounds, which can lead to conflicts and debates.
- Inequality: Mandatory army service can disproportionately affect certain groups, such as low-income citizens or those from minority backgrounds.
- Economic impact: Mandatory army service can have significant economic impacts, both positive and negative, depending on the country and its economy.

Examples of Mandatory Army Service
Several countries have implemented mandatory army service systems, each with its unique characteristics and challenges. Here are a few examples:
- Israel: Israel has a mandatory army service system that lasts for 2 years for men and 2 years for women. Citizens are required to register at age 18 and can be exempted for medical or religious reasons.
- South Korea: South Korea has a mandatory army service system that lasts for 18 months for men and 2 years for women. Citizens are required to register at age 18 and can be exempted for medical or educational reasons.
- Greece: Greece has a mandatory army service system that lasts for 9 months for men and 6 months for women. Citizens are required to register at age 19 and can be exempted for medical or family reasons.

Alternatives to Mandatory Army Service
Some countries have abolished mandatory army service or introduced alternative systems. For example:
- Austria: Austria abolished mandatory army service in 1971 and introduced a professional military instead.
- Germany: Germany introduced a professional military in 2011 and abolished mandatory army service.
- Sweden: Sweden introduced a professional military in 2010 and abolished mandatory army service.

Conclusion
Mandatory army service is a complex and multifaceted issue that has both benefits and drawbacks. While it can provide valuable skills and civic engagement, it can also be challenging and controversial. As countries continue to grapple with the pros and cons of mandatory army service, it's essential to consider the unique needs and circumstances of each nation.

Mandatory Army Service Gallery
Mandatory Army Service Image Gallery










Frequently Asked Questions
What is mandatory army service?
+Mandatory army service is a system where citizens are required to serve in the military for a certain period.
How long does mandatory army service last?
+The length of mandatory army service varies from country to country, but it typically ranges from 1 to 3 years.
What are the benefits of mandatory army service?
+Mandatory army service can provide valuable skills, civic engagement, and national security.
