Intro
US inflation rate surges to 2.9%, exceeding expectations. Understand the implications of rising inflation on interest rates, consumer spending, and the economy. Learn how to navigate the increasing costs of living and potential recession risks. Get expert insights on the inflation rates impact on your finances and investments.
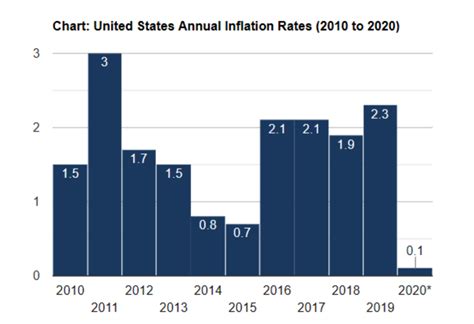
The United States inflation rate has been a topic of discussion in recent months, and the latest numbers have sparked concerns among economists and consumers alike. The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) recently announced that the inflation rate rose to 2.9% in June, marking a six-year high. But what does this mean for the average American, and how will it impact the economy?
The current inflation rate is significantly higher than the 2.4% rate seen in March, and it exceeds the Federal Reserve's target rate of 2%. This surge in inflation is largely attributed to the steady growth of the US economy, which has been fueled by a strong labor market, rising wages, and increased consumer spending. However, some experts argue that the inflation rate is rising too quickly, and that it could have negative consequences for the economy.
Understanding Inflation
Inflation is a complex economic concept that can be difficult to grasp. Simply put, inflation is the rate at which prices for goods and services are rising. As inflation increases, the purchasing power of consumers decreases, meaning that the same amount of money can buy fewer goods and services.
Inflation is measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI), which tracks the prices of a basket of goods and services. The CPI includes prices for food, housing, clothing, transportation, and other essential items. The inflation rate is calculated by comparing the current CPI to the previous month's CPI.
Causes of Inflation
There are several factors that contribute to inflation. Some of the main causes of inflation include:
- Demand and supply imbalance: When demand for goods and services exceeds supply, businesses can raise their prices, leading to inflation.
- Economic growth: A rapidly growing economy can lead to increased demand for goods and services, resulting in higher prices.
- Monetary policy: The Federal Reserve's decision to lower interest rates or increase the money supply can lead to inflation.
- External shocks: Events such as natural disasters, global conflicts, or supply chain disruptions can lead to price increases.
Impact of Inflation on Consumers
Inflation can have a significant impact on consumers, particularly those living on a fixed income or with limited financial resources. As prices rise, consumers may find it difficult to afford the same goods and services that they previously enjoyed. This can lead to a decrease in their standard of living.
Some of the ways that inflation can affect consumers include:
- Reduced purchasing power: As prices rise, the same amount of money can buy fewer goods and services.
- Increased cost of living: Inflation can lead to higher costs for essential items such as housing, food, and healthcare.
- Uncertainty: Inflation can create uncertainty and anxiety for consumers, making it difficult for them to budget and plan for the future.
Impact of Inflation on Businesses
Inflation can also have a significant impact on businesses, particularly those with thin profit margins or limited pricing power. As prices rise, businesses may struggle to maintain their profit margins, leading to decreased earnings and reduced competitiveness.
Some of the ways that inflation can affect businesses include:
- Increased costs: Inflation can lead to higher costs for raw materials, labor, and other essential inputs.
- Reduced profit margins: As prices rise, businesses may struggle to maintain their profit margins, leading to decreased earnings.
- Uncertainty: Inflation can create uncertainty and anxiety for businesses, making it difficult for them to budget and plan for the future.
Strategies for Businesses to Mitigate Inflation
There are several strategies that businesses can use to mitigate the impact of inflation. Some of these strategies include:
- Diversifying suppliers: Businesses can reduce their dependence on a single supplier by diversifying their supply chain.
- Increasing prices: Businesses can increase their prices to keep pace with inflation, but this can be a difficult decision, particularly in competitive markets.
- Investing in technology: Businesses can invest in technology to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
- Diversifying products: Businesses can diversify their products to reduce their dependence on a single product or market.

Monetary Policy and Inflation
The Federal Reserve plays a critical role in managing inflation through monetary policy. The Fed's primary tools for managing inflation are interest rates and the money supply.
When inflation rises, the Fed may increase interest rates to reduce borrowing and spending, which can help to slow down the economy and reduce inflation. Conversely, when inflation falls, the Fed may lower interest rates to stimulate borrowing and spending, which can help to boost the economy and increase inflation.
The Role of Fiscal Policy in Managing Inflation
Fiscal policy also plays a critical role in managing inflation. Fiscal policy refers to the use of government spending and taxation to manage the economy.
When inflation rises, the government may reduce its spending or increase taxes to reduce demand and slow down the economy. Conversely, when inflation falls, the government may increase its spending or cut taxes to boost demand and stimulate the economy.

Conclusion
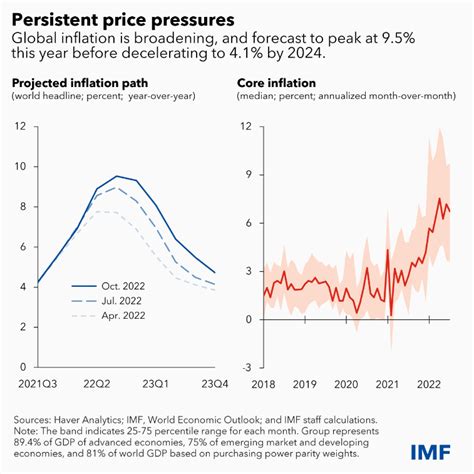
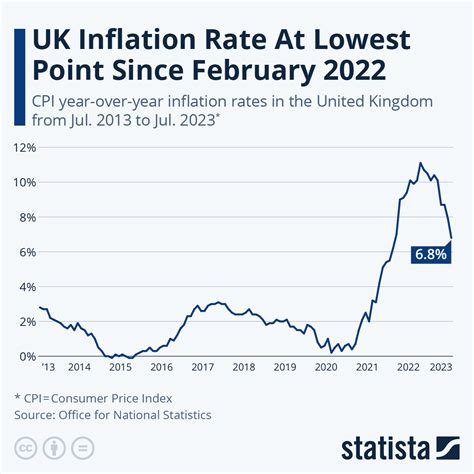
The recent rise in the US inflation rate to 2.9% has sparked concerns among economists and consumers alike. While inflation can have negative consequences for consumers and businesses, it is also a sign of a growing economy.
Understanding the causes and impact of inflation is critical for consumers, businesses, and policymakers. By understanding the factors that contribute to inflation and the strategies for mitigating its impact, we can work together to create a more stable and prosperous economy.
Inflation Rate Image Gallery




What is inflation?
+Inflation is the rate at which prices for goods and services are rising.
What causes inflation?
+Inflation is caused by a variety of factors, including demand and supply imbalance, economic growth, monetary policy, and external shocks.
How does inflation affect consumers?
+Inflation can reduce the purchasing power of consumers, increase the cost of living, and create uncertainty and anxiety.
