Intro
Discover the rich history and proud heritage of the US Army, Americas oldest branch of service. From its founding in 1775 to present day, explore the Armys evolution, notable conflicts, and legendary figures. Learn about its role in shaping the nations defense and the values that define its soldiers, including patriotism, duty, and selfless service.
The United States Army is the oldest branch of the US military, with a rich history that dates back to the American Revolutionary War. Established on June 14, 1775, the Continental Army was formed to fight against the British Empire, and it has since evolved into the modern US Army. Today, the Army is one of the largest and most technologically advanced militaries in the world, with a proud legacy of serving the nation and protecting its interests.
The Army's origins can be traced back to the earliest days of the American Revolution, when the Continental Congress authorized the creation of a continental army to defend the newly independent colonies against British rule. The Army's first commander, George Washington, was appointed on June 15, 1775, and he played a crucial role in shaping the Continental Army into a formidable fighting force.

Throughout its history, the US Army has undergone numerous transformations, adapting to changing circumstances and emerging technologies. During the Civil War, the Army played a critical role in preserving the Union, while World War I and World War II saw the Army expand its scope and scale, becoming a global military presence.
Key Functions and Responsibilities
As the oldest branch of the US military, the Army is responsible for a wide range of functions and responsibilities. Some of the key duties include:
-
Land-Based Operations
The Army is the primary land-based military force, responsible for conducting operations on the ground, in the air, and in space. Its main mission is to protect the nation and its interests by deterring aggression, promoting stability, and defending against threats.
-
Homeland Defense
The Army plays a vital role in homeland defense, working closely with other government agencies to prevent and respond to domestic threats, such as terrorism and natural disasters.
-
Disaster Relief and Humanitarian Assistance
The Army provides critical support during natural disasters and humanitarian crises, both within the US and abroad. Its personnel and equipment are often deployed to provide aid, support, and relief to affected communities.
-
Training and Education
The Army is responsible for training and educating its personnel, ensuring they have the skills and knowledge needed to perform their duties effectively. The Army also provides training and education to other military branches and international partners.

Organizational Structure
The US Army is organized into several key components, including:
-
Active Duty
The Active Duty component consists of full-time soldiers who serve on a continuous basis. These soldiers are responsible for performing a wide range of duties, from combat operations to support roles.
-
Reserve
The Reserve component is comprised of part-time soldiers who serve on a limited basis. These soldiers are typically called upon to support Active Duty personnel during times of war or crisis.
-
National Guard
The National Guard is a reserve component that serves both federal and state governments. Its personnel can be deployed to support domestic emergencies, such as natural disasters, and international operations.
-
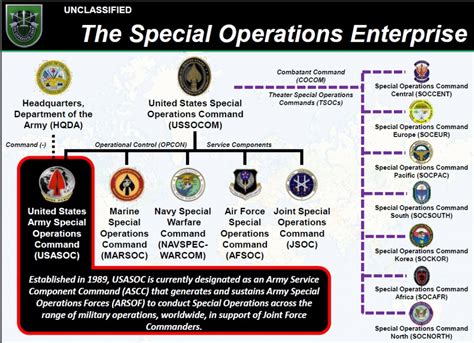
Special Operations Forces
The Army's Special Operations Forces (SOF) are elite units that conduct specialized missions, such as counterterrorism, direct action, and special reconnaissance.

Equipment and Technology
The US Army is equipped with some of the most advanced technology and equipment in the world, including:
-
Tanks and Armored Vehicles
The Army operates a range of tanks and armored vehicles, including the M1 Abrams and the M2 Bradley.
-
Artillery and Firearms
The Army uses a variety of artillery systems, including the M109 Paladin and the M777 Howitzer, as well as firearms such as the M4 carbine and the M240 machine gun.
-
Aircraft and Helicopters
The Army operates a range of aircraft and helicopters, including the UH-60 Black Hawk, the AH-64 Apache, and the CH-47 Chinook.
-
Communication Systems
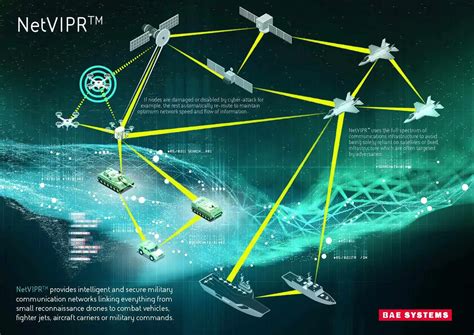
The Army uses advanced communication systems, including satellite communications and secure networks, to coordinate operations and share information.

Notable Operations and Conflicts
Throughout its history, the US Army has been involved in numerous notable operations and conflicts, including:
-
American Revolutionary War
The Army's first major conflict, in which it fought against the British Empire to secure American independence.
-
Civil War
The Army played a critical role in preserving the Union during the Civil War, which lasted from 1861 to 1865.
-
World War I and World War II
The Army expanded its scope and scale during these global conflicts, playing a key role in the Allied victory.
-
Korean War and Vietnam War
The Army was involved in these conflicts, which took place in the mid-20th century.
-
Gulf War and Iraq War
The Army played a major role in these conflicts, which took place in the late 20th and early 21st centuries.
Conclusion
The US Army is a proud and storied institution, with a rich history and a legacy of serving the nation. From its humble beginnings as the Continental Army to its current status as a global military power, the Army has consistently demonstrated its commitment to protecting American interests and promoting stability around the world.
US Army Image Gallery








What is the primary mission of the US Army?
+The primary mission of the US Army is to protect the nation and its interests by deterring aggression, promoting stability, and defending against threats.
What is the difference between the Active Duty and Reserve components of the US Army?
+The Active Duty component consists of full-time soldiers who serve on a continuous basis, while the Reserve component is comprised of part-time soldiers who serve on a limited basis.
What is the role of the US Army in homeland defense?
+The US Army plays a critical role in homeland defense, working closely with other government agencies to prevent and respond to domestic threats, such as terrorism and natural disasters.
What is the US Army's policy on cybersecurity and network defense?
+The US Army takes cybersecurity and network defense seriously, with a focus on protecting its networks and systems from cyber threats and ensuring the security of its operations.
How does the US Army support disaster relief and humanitarian assistance efforts?
+The US Army provides critical support during natural disasters and humanitarian crises, both within the US and abroad, through the deployment of personnel and equipment.
