Intro
Discover 5 significant Islamic events, including Eid al-Fitr, Hajj, and Ramadan, exploring their history, significance, and spiritual importance in Islam, with insights into Islamic culture and traditions.
The Islamic calendar is filled with significant events that hold great importance for Muslims around the world. These events are a testament to the rich history and spiritual depth of Islam, and they continue to inspire and guide Muslims in their daily lives. In this article, we will explore five major Islamic events that are observed with great fervor and dedication by Muslims globally.
The Islamic calendar is based on the lunar cycle, and it is approximately 11 days shorter than the solar calendar used in the Western world. This means that Islamic events and holidays appear to shift each year when viewed from a Western perspective. However, for Muslims, the timing of these events is carefully calculated and anticipated, as they are deeply rooted in the Islamic faith and practice.
The significance of these events lies not only in their historical and cultural importance but also in the spiritual lessons and values they impart. They remind Muslims of the importance of faith, compassion, forgiveness, and self-reflection, among other virtues. By observing these events, Muslims strengthen their connection with their faith and with the global Muslim community, fostering a sense of unity and solidarity.
Introduction to Islamic Events
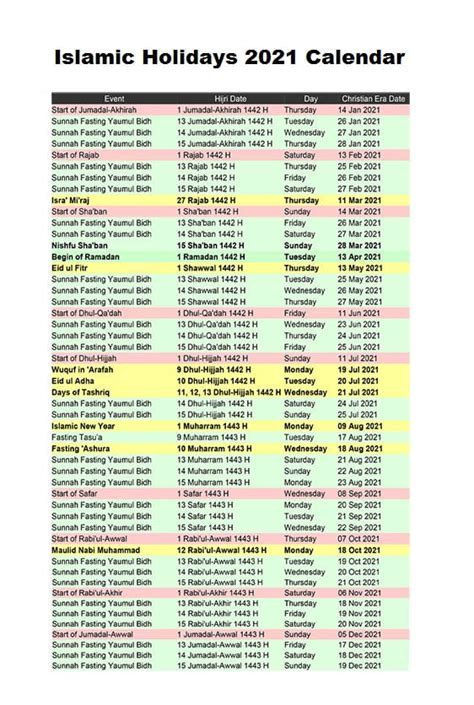
Understanding the context and significance of Islamic events is crucial for appreciating the diversity and richness of Islamic culture and tradition. These events are often marked by specific rituals, practices, and celebrations that vary across different Muslim communities, reflecting the beautiful tapestry of Islamic practices worldwide.
1. Eid al-Fitr

Eid al-Fitr, or the "Festival of Breaking the Fast," is one of the most significant Islamic events. It marks the end of Ramadan, the holy month of fasting, and is a time of great joy and celebration. Muslims wake up early in the morning, perform a special prayer, and then gather with family and friends to exchange gifts and share meals. The essence of Eid al-Fitr is the celebration of the completion of the fasting month, during which Muslims abstain from food and drink from dawn to sunset, seeking to strengthen their faith and connection with Allah.
The practices during Eid al-Fitr include:
- Performing the Eid prayer in congregation
- Giving charity to the poor, known as Zakat al-Fitr
- Spending time with family and friends
- Exchanging gifts, especially with children
- Engaging in acts of kindness and generosity
2. Eid al-Adha

Eid al-Adha, or the "Festival of the Sacrifice," commemorates the willingness of the Prophet Ibrahim (Abraham) to sacrifice his son Ismail (Ishmael) as an act of obedience to God's command. It is a celebration of faith, obedience, and the willingness to sacrifice for one's beliefs. During Eid al-Adha, Muslims slaughter an animal (usually a sheep, goat, or cow) as a symbol of Ibrahim's sacrifice, distributing the meat among family, friends, and the poor.
The significance of Eid al-Adha lies in its reminder of the importance of submission to Allah's will and the value of selflessness and compassion. The practices associated with Eid al-Adha include:
- Performing the Eid prayer
- Sacrificing an animal (for those who can afford it)
- Distributing meat to the needy
- Visiting family and friends
- Engaging in acts of charity and kindness
3. Laylat al-Mi'raj

Laylat al-Mi'raj, or the "Night of Ascension," marks the occasion when the Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him) ascended to heaven from the Masjid al-Aqsa in Jerusalem. This event is considered a pivotal moment in Islamic history, as it was during this journey that the Prophet received revelations and instructions from Allah, including the command to perform the five daily prayers.
The celebration of Laylat al-Mi'raj involves:
- Reciting the Quran and performing extra prayers
- Engaging in acts of worship and remembrance of Allah
- Reflecting on the significance of the Prophet's journey and its implications for Muslim life
- Gathering for communal prayers and lectures
4. Laylat al-Bara'ah

Laylat al-Bara'ah, or the "Night of Forgiveness," is observed on the 15th of the Islamic month of Sha'ban. It is believed to be a night when Allah forgives the sins of believers and determines their provisions for the upcoming year. Muslims spend this night in prayer, seeking forgiveness, and engaging in acts of worship.
The practices during Laylat al-Bara'ah include:
- Performing extra prayers and reciting the Quran
- Seeking forgiveness from Allah for past sins
- Engaging in charity and good deeds
- Visiting graves to pray for the deceased
5. Ashura

Ashura is commemorated on the 10th of Muharram, the first month of the Islamic calendar. It marks the martyrdom of Imam Hussein, the grandson of the Prophet Muhammad, who was killed in the Battle of Karbala. For Shia Muslims, Ashura is a day of mourning and remembrance, while for Sunni Muslims, it is a day of fasting and reflection.
The observance of Ashura involves:
- Fasting on the 10th of Muharram (for Sunni Muslims)
- Mourning and processions (for Shia Muslims)
- Visiting mosques and shrines
- Engaging in acts of charity and kindness
Islamic Events Image Gallery










What is the significance of Eid al-Fitr?
+Eid al-Fitr marks the end of Ramadan, the holy month of fasting, and is a celebration of the completion of this spiritual journey. It emphasizes the values of gratitude, generosity, and unity among Muslims.
How do Muslims observe Laylat al-Mi'raj?
+Muslims observe Laylat al-Mi'raj by engaging in extra prayers, reciting the Quran, and reflecting on the significance of the Prophet Muhammad's ascension to heaven. It is a night of worship and remembrance.
What is the difference between Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha?
+Eid al-Fitr marks the end of Ramadan and is a celebration of the completion of fasting, while Eid al-Adha commemorates the willingness of Prophet Ibrahim to sacrifice his son and is a celebration of faith, obedience, and sacrifice.
As we delve into the significance and observance of these Islamic events, it becomes clear that they are not just historical commemorations but living practices that shape the daily lives and spiritual journeys of Muslims. They serve as reminders of the core values of Islam, such as compassion, forgiveness, and submission to Allah's will. By understanding and appreciating these events, we can foster greater respect and unity among people of different backgrounds and faiths. We invite our readers to share their thoughts and reflections on these significant Islamic events and to explore the richness and diversity of Islamic culture and tradition.
