Intro
Discover the crucial role of case workers in supporting vulnerable populations. Learn about the roles and responsibilities of case workers, including assessment, planning, and advocacy, and how they coordinate services to promote client well-being. Explore the skills and qualifications required to succeed in this rewarding field.
Case workers play a vital role in various social services, healthcare, and non-profit organizations, providing essential support to individuals, families, and communities in need. Despite their importance, many people are unclear about the roles and responsibilities of case workers. In this article, we will delve into the world of case work, exploring the key aspects of this profession and shedding light on the crucial tasks they perform.
What is a Case Worker?
A case worker, also known as a social worker or case manager, is a trained professional who provides assistance and support to individuals, families, or groups who are facing challenges or difficulties. These challenges may include poverty, mental health issues, addiction, disability, or other forms of adversity. Case workers operate in a variety of settings, such as hospitals, clinics, non-profit organizations, government agencies, and community centers.
Key Roles and Responsibilities of Case Workers
The primary goal of a case worker is to empower individuals and families to overcome obstacles and improve their overall well-being. To achieve this, case workers perform a range of tasks, including:
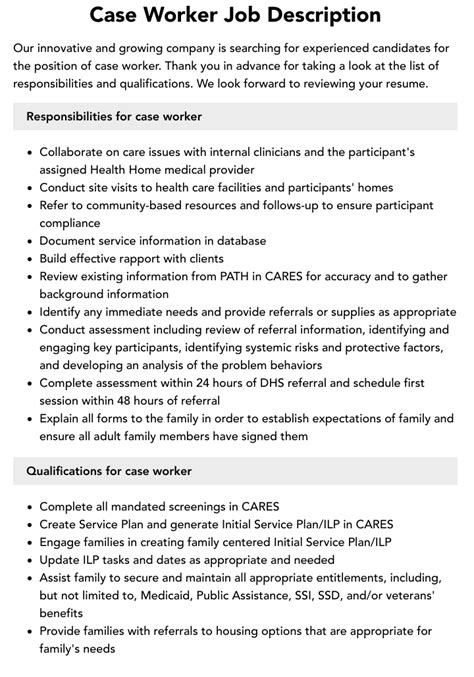
- Assessment and Intake: Case workers conduct initial assessments to identify the needs and concerns of their clients. They gather information about the individual's or family's situation, including their strengths, weaknesses, and goals.
- Goal Setting: Based on the assessment, case workers collaborate with their clients to set realistic goals and develop a plan to achieve them.
- Service Coordination: Case workers connect their clients with relevant services, such as healthcare, education, and employment opportunities. They also facilitate access to community resources, like food banks, housing assistance, and counseling services.
- Counseling and Support: Case workers provide emotional support, guidance, and counseling to help their clients cope with challenges and develop coping strategies.
- Advocacy: Case workers advocate on behalf of their clients, ensuring their rights are respected and their needs are met.
The Benefits of Working with a Case Worker
Engaging with a case worker can have a significant impact on an individual's or family's life. Some of the benefits of working with a case worker include:
- Improved access to services: Case workers can help individuals and families access essential services, such as healthcare, education, and employment opportunities.
- Increased support: Case workers provide emotional support, guidance, and counseling to help individuals and families cope with challenges.
- Empowerment: Case workers empower their clients to take control of their lives, make informed decisions, and develop the skills needed to overcome obstacles.
- Improved outcomes: Working with a case worker can lead to better outcomes, such as improved health, increased stability, and enhanced overall well-being.

Case Worker Specializations
Case workers can specialize in various areas, including:
- Child welfare: Working with children and families to ensure their safety and well-being.
- Mental health: Providing support and services to individuals with mental health conditions.
- Substance abuse: Helping individuals struggling with addiction to access treatment and support services.
- Disability: Supporting individuals with disabilities to access resources and services that promote independence and inclusion.
- Gerontology: Working with older adults to address their unique needs and challenges.
Case Worker Skills and Qualifications
To become a case worker, one typically requires:
- Education: A bachelor's degree in social work, psychology, or a related field.
- Training: Completion of a training program or certification in case work.
- Skills: Strong communication, interpersonal, and problem-solving skills.
- Compassion: A genuine desire to help others and make a positive difference in their lives.

Challenges Facing Case Workers
Despite the rewards of being a case worker, this profession comes with its own set of challenges, including:
- High caseloads: Managing a large number of clients can be overwhelming and stressful.
- Limited resources: Case workers often face budget constraints and limited access to resources, making it difficult to provide the necessary support.
- Emotional demands: Working with vulnerable populations can be emotionally draining and traumatic.
- Bureaucratic barriers: Navigating complex systems and paperwork can hinder the case worker's ability to provide effective support.
Conclusion
Case workers play a vital role in supporting individuals, families, and communities in need. By understanding the roles and responsibilities of case workers, we can appreciate the importance of this profession and the positive impact it has on people's lives. If you are considering a career as a case worker, remember that it requires a unique blend of skills, knowledge, and compassion. With dedication and hard work, you can make a real difference in the lives of others.
Case Worker Image Gallery






What is the primary role of a case worker?
+The primary role of a case worker is to provide support and services to individuals, families, or groups who are facing challenges or difficulties.
What are the benefits of working with a case worker?
+Working with a case worker can provide improved access to services, increased support, empowerment, and better outcomes.
What skills and qualifications are required to become a case worker?
+To become a case worker, one typically requires a bachelor's degree in social work or a related field, training or certification in case work, and strong communication, interpersonal, and problem-solving skills.
