Intro
Discover the world of job shop manufacturing, a production process that enables flexible, small-batch production of customized products. Learn how job shops operate, their benefits, and the key differences between job shop and other manufacturing processes, including batch and continuous production. Optimize your production strategy with expert insights.
In today's fast-paced and highly competitive manufacturing landscape, companies are constantly seeking ways to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and increase productivity. One approach that has gained popularity in recent years is job shop manufacturing. In this article, we will delve into the world of job shop manufacturing, exploring its benefits, working mechanisms, and key considerations for implementation.
What is Job Shop Manufacturing?

Job shop manufacturing is a production methodology that involves the processing of small batches or one-off orders in a workshop or factory setting. This approach is ideal for companies that produce a wide variety of products or components, often with complex designs or unique specifications. Job shops typically operate on a project-by-project basis, with each project requiring a distinct set of processes, materials, and equipment.
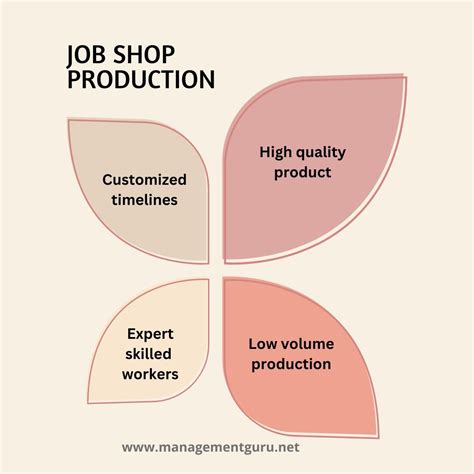
Benefits of Job Shop Manufacturing
There are several benefits associated with job shop manufacturing, including:
- Flexibility: Job shops can quickly adapt to changes in production schedules, product designs, or material specifications.
- Low Volume Production: Job shops are well-suited for producing small batches or one-off orders, making them ideal for companies with diverse product lines.
- High Product Mix: Job shops can handle a wide range of products or components, often with complex designs or unique specifications.
- Reduced Lead Times: Job shops can reduce lead times by prioritizing projects and allocating resources efficiently.
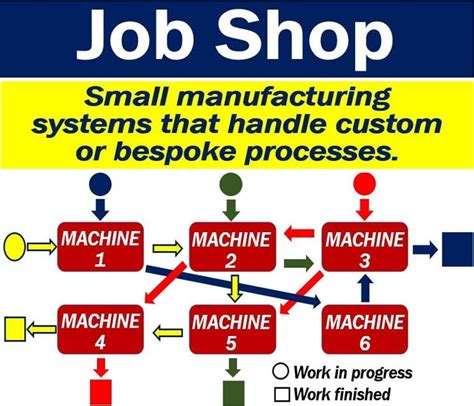
How Does Job Shop Manufacturing Work?
The job shop manufacturing process typically involves the following steps:
- Project Planning: The job shop receives a project request from a customer, which includes product specifications, material requirements, and production deadlines.
- Process Planning: The job shop creates a detailed process plan, outlining the necessary steps, equipment, and personnel required to complete the project.
- Material Procurement: The job shop procures the necessary materials and components for the project.
- Production: The job shop produces the product or component, following the process plan and using the allocated equipment and personnel.
- Quality Control: The job shop conducts quality control checks to ensure the product meets customer specifications and quality standards.
- Delivery: The job shop delivers the finished product to the customer.
Key Considerations for Job Shop Manufacturing
When implementing job shop manufacturing, companies should consider the following factors:
- Equipment and Technology: Job shops require a range of equipment and technology to support diverse production processes.
- Skilled Labor: Job shops require skilled labor with expertise in various production processes and techniques.
- Material Management: Job shops must manage material inventory and procurement to ensure timely delivery of projects.
- Project Management: Job shops require effective project management to prioritize projects, allocate resources, and meet production deadlines.
Challenges and Limitations of Job Shop Manufacturing

While job shop manufacturing offers several benefits, it also presents some challenges and limitations, including:
- High Overhead Costs: Job shops often have high overhead costs due to the need for diverse equipment and skilled labor.
- Low Efficiency: Job shops can experience low efficiency due to the frequent changeovers and setup times required for different projects.
- Difficulty in Scaling: Job shops can struggle to scale production due to the complexity and variability of projects.
Real-World Applications of Job Shop Manufacturing

Job shop manufacturing is widely used in various industries, including:
- Aerospace: Job shops produce complex components and assemblies for aircraft and spacecraft.
- Automotive: Job shops produce custom parts and components for the automotive industry.
- Medical Devices: Job shops produce complex medical devices and equipment.
- Consumer Products: Job shops produce custom products, such as furniture and fixtures.
Best Practices for Implementing Job Shop Manufacturing
To successfully implement job shop manufacturing, companies should follow these best practices:
- Develop a Clear Project Plan: Create a detailed project plan, outlining the necessary steps, equipment, and personnel required to complete the project.
- Invest in Technology: Invest in technology, such as computer-aided design (CAD) software and computer numerical control (CNC) machines, to support diverse production processes.
- Train Skilled Labor: Train skilled labor with expertise in various production processes and techniques.
- Implement Material Management: Implement material management systems to ensure timely delivery of projects.
Job Shop Manufacturing Image Gallery





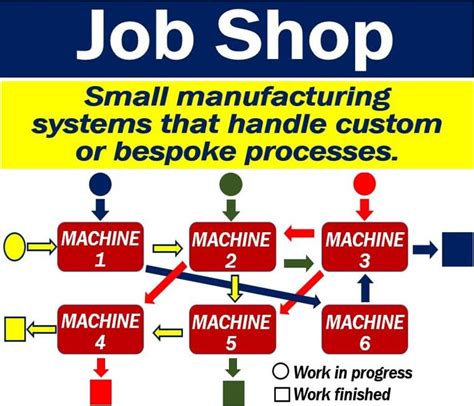

What is job shop manufacturing?
+Job shop manufacturing is a production methodology that involves the processing of small batches or one-off orders in a workshop or factory setting.
What are the benefits of job shop manufacturing?
+The benefits of job shop manufacturing include flexibility, low volume production, high product mix, and reduced lead times.
What are the challenges and limitations of job shop manufacturing?
+The challenges and limitations of job shop manufacturing include high overhead costs, low efficiency, and difficulty in scaling.
In conclusion, job shop manufacturing is a flexible and versatile production methodology that can help companies improve efficiency, reduce costs, and increase productivity. By understanding the benefits, working mechanisms, and key considerations of job shop manufacturing, companies can successfully implement this approach and achieve their production goals.
