Intro
Discover the fascinating history behind the term cockpit in aviation. Learn about the 5 key reasons how this crucial compartment got its name, from its origins in naval warfare to its evolution in aircraft design. Explore the intriguing connections between cockpit, ships steering, and more, and uncover the surprising roots of this ubiquitous aviation term.
The term "cockpit" is a familiar one in the world of aviation, but have you ever stopped to think about how it got its name? The origin of the term "cockpit" is a fascinating story that dates back to the early days of aviation. In this article, we'll explore the history behind the term "cockpit" and examine the five reasons why it became the standard term used in aviation today.
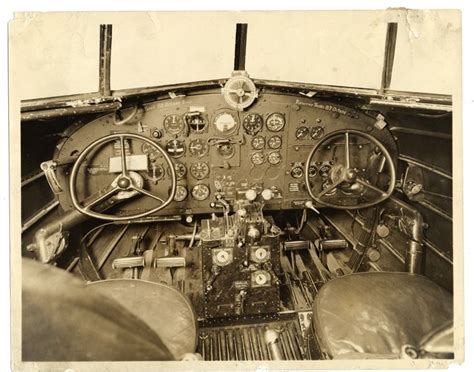
Reason 1: Early Aviation Roots
The term "cockpit" has its roots in the early days of aviation, when aircraft were essentially modified versions of World War I fighter planes. The first aircraft were designed with a single seat for the pilot, who sat in a small compartment that resembled a bathtub. This compartment was initially called the "cockpit" due to its resemblance to the cockpit of a sailing ship.
Reason 2: Sailing Ship Influence
In the 17th and 18th centuries, sailing ships had a small compartment on the deck called the "cockpit" where the ship's wheel and navigation equipment were located. The compartment was called the "cockpit" because it was where the ship's crew would gather to navigate the vessel, much like a cockpit in a modern aircraft. When aircraft designers began building their own flying machines, they drew inspiration from sailing ships and adopted the term "cockpit" for the pilot's compartment.
Reason 3: Pilot Protection
Another reason the term "cockpit" stuck was due to the need for pilot protection. In the early days of aviation, aircraft were open-cockpit designs, with the pilot exposed to the elements. As aircraft design evolved, the cockpit became a more enclosed space, providing better protection for the pilot from wind, rain, and other hazards. The term "cockpit" emphasized the importance of this protective space for the pilot.
Reason 4: Multi-Crew Operations
As aircraft became more complex and multi-crew operations became more common, the term "cockpit" took on a new significance. The cockpit was no longer just a small compartment for a single pilot but a shared space for multiple crew members to work together. The term "cockpit" acknowledged this shift towards multi-crew operations and the need for coordination and communication between crew members.
Reason 5: Standardization
Finally, the term "cockpit" became the standard term used in aviation due to the need for standardization. As aviation grew into a global industry, standardization became essential for safety and efficiency. The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) and other regulatory bodies adopted the term "cockpit" as the official term for the pilot's compartment, cementing its place in the lexicon of aviation.
Understanding Cockpit Design

In modern aircraft, the cockpit is a highly sophisticated space that requires careful design and planning. Cockpit design involves a deep understanding of human factors, ergonomics, and user experience. The goal of cockpit design is to create a safe, efficient, and intuitive workspace for pilots to operate the aircraft.
Key Principles of Cockpit Design
- Ergonomics: The cockpit must be designed to accommodate the physical needs of the pilot, including seat height, armrests, and control placement.
- Visibility: The cockpit must provide excellent visibility for the pilot, including forward visibility, side visibility, and rear visibility.
- Accessibility: The cockpit must be designed to facilitate easy access to controls, instruments, and other essential systems.
- Intuitiveness: The cockpit must be intuitive to use, with clear and concise labeling, and logical placement of controls and instruments.
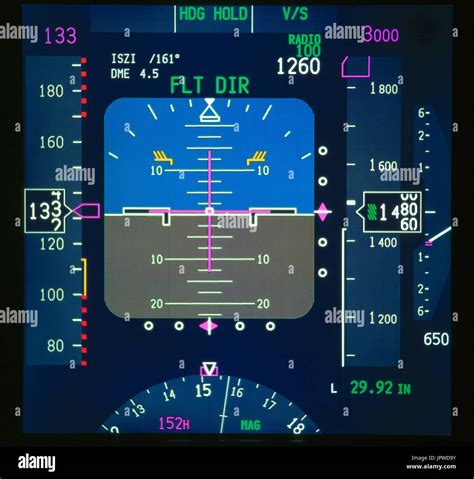
Cockpit Technology Advances
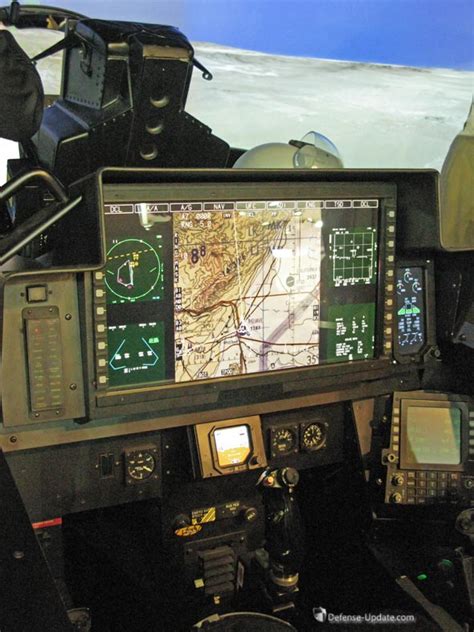

The cockpit has undergone significant technological advances in recent years, driven by the need for improved safety, efficiency, and pilot workload reduction. Some of the key advances in cockpit technology include:
- Glass cockpits: Modern aircraft often feature glass cockpits, which replace traditional mechanical instruments with electronic displays.
- Fly-by-wire systems: Fly-by-wire systems use electronic signals to control the aircraft, reducing pilot workload and improving safety.
- Advanced avionics: Modern aircraft often feature advanced avionics, including GPS, autopilot, and weather radar.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the term "cockpit" has a rich history that reflects the evolution of aviation. From its roots in sailing ships to its modern application in aircraft design, the term "cockpit" has become an integral part of the aviation lexicon. By understanding the five reasons behind the term "cockpit," we can appreciate the complexity and sophistication of modern aircraft design.
Cockpit Image Gallery









What is the origin of the term "cockpit"?
+The term "cockpit" has its roots in the early days of aviation, when aircraft were essentially modified versions of World War I fighter planes. The first aircraft were designed with a single seat for the pilot, who sat in a small compartment that resembled a bathtub.
What are the key principles of cockpit design?
+The key principles of cockpit design include ergonomics, visibility, accessibility, and intuitiveness. The cockpit must be designed to accommodate the physical needs of the pilot, provide excellent visibility, facilitate easy access to controls and instruments, and be intuitive to use.
What are some advances in cockpit technology?
+Some advances in cockpit technology include glass cockpits, fly-by-wire systems, and advanced avionics. These technologies have improved safety, efficiency, and pilot workload reduction.
