Intro
Discover the 5 biggest WW1 sea battles that shaped the course of history. From the Battle of Jutland to the Battle of Dogger Bank, explore the most significant naval clashes of World War I, including the role of dreadnoughts, U-boats, and Allied convoys, and how they impacted the wars outcome.
The Great War, also known as World War I, was a global conflict that lasted from 1914 to 1918. While many people are familiar with the trenches and battles on land, the war also saw significant naval battles that played a crucial role in the outcome of the conflict. Here, we'll explore the 5 biggest WW1 sea battles that shaped the course of history.

The naval war was fought on multiple fronts, including the North Sea, the Baltic Sea, the Mediterranean, and the Atlantic Ocean. The war saw the introduction of new technologies, such as submarines, aircraft carriers, and dreadnought battleships, which changed the face of naval warfare. Here are the 5 biggest WW1 sea battles that had a significant impact on the war:
The Battle of Heligoland Bight (August 28, 1914)
The Battle of Heligoland Bight was one of the first major naval battles of World War I. It took place in the North Sea, off the coast of Germany, and involved British and German warships. The British aim was to destroy the German naval presence in the area and secure the North Sea for Allied shipping.

The British fleet, consisting of 30 destroyers and 8 cruisers, was led by Commodore Reginald Tyrwhitt. The German fleet, consisting of 12 destroyers and 6 cruisers, was led by Commodore Leberecht Maass. The battle was fierce, with both sides suffering losses. However, the British emerged victorious, sinking three German cruisers and one destroyer.
The Battle of Coronel (November 1, 1914)
The Battle of Coronel was a naval battle fought off the coast of Chile, in the Pacific Ocean. It was one of the first major naval battles of World War I, and it saw the German East Asia Squadron, led by Admiral Maximilian von Spee, clash with the British Royal Navy.

The German squadron consisted of two armored cruisers, three light cruisers, and three torpedo boats. The British fleet, led by Rear Admiral Christopher Cradock, consisted of two armored cruisers, a light cruiser, and a converted liner. The battle was intense, with the Germans sinking two British armored cruisers. However, the Germans suffered significant losses, including the sinking of one of their own armored cruisers.
The Battle of Dogger Bank (January 24, 1915)
The Battle of Dogger Bank was a naval battle fought in the North Sea, off the coast of Denmark. It was one of the largest naval battles of World War I, involving over 100 ships from both the British and German navies.
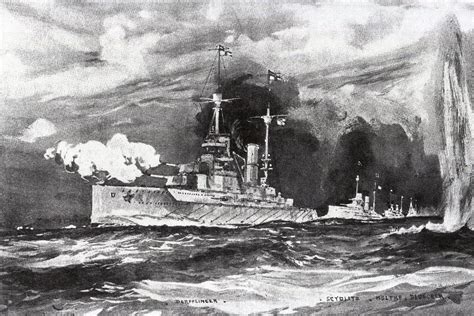
The British fleet, led by Admiral Sir David Beatty, consisted of five battlecruisers, seven light cruisers, and 35 destroyers. The German fleet, led by Admiral Franz von Hipper, consisted of three battlecruisers, four light cruisers, and 18 destroyers. The battle was fierce, with both sides suffering losses. However, the British emerged victorious, sinking one German battlecruiser and damaging several other ships.
The Battle of Jutland (May 31-June 1, 1916)
The Battle of Jutland was one of the largest naval battles of World War I, involving over 250 ships from both the British and German navies. It was fought in the North Sea, off the coast of Denmark, and saw the British Grand Fleet clash with the German High Seas Fleet.

The British fleet, led by Admiral Sir John Jellicoe, consisted of 28 battleships, nine battlecruisers, eight armored cruisers, and 26 light cruisers. The German fleet, led by Admiral Reinhard Scheer, consisted of 16 battleships, six battlecruisers, six pre-dreadnought battleships, and 61 torpedo boats. The battle was intense, with both sides suffering significant losses. However, the British emerged victorious, sinking 11 German ships, including one battleship and three battlecruisers.
The Battle of the Strait of Otranto (May 15, 1917)
The Battle of the Strait of Otranto was a naval battle fought in the Adriatic Sea, off the coast of Italy. It was one of the largest naval battles of World War I, involving over 150 ships from both the Austro-Hungarian and Allied navies.

The Austro-Hungarian fleet, led by Admiral Miklós Horthy, consisted of three battleships, four cruisers, and 24 torpedo boats. The Allied fleet, led by Admiral Alfredo Acton, consisted of 40 destroyers, 16 torpedo boats, and several patrol boats. The battle was intense, with both sides suffering losses. However, the Austro-Hungarians emerged victorious, sinking 14 Allied ships, including two destroyers and several patrol boats.
These five battles were some of the largest and most significant naval battles of World War I. They saw the introduction of new technologies, such as submarines and aircraft carriers, and changed the face of naval warfare. The battles also had a significant impact on the outcome of the war, with the Allies ultimately emerging victorious.
Gallery of World War 1 Sea Battles
World War 1 Sea Battles Image Gallery









What was the significance of the Battle of Heligoland Bight?
+The Battle of Heligoland Bight was significant because it was one of the first major naval battles of World War I, and it saw the British Royal Navy emerge victorious against the German Navy.
What was the outcome of the Battle of Coronel?
+The Battle of Coronel was a victory for the German East Asia Squadron, led by Admiral Maximilian von Spee. The Germans sank two British armored cruisers, but suffered significant losses, including the sinking of one of their own armored cruisers.
What was the significance of the Battle of Jutland?
+The Battle of Jutland was one of the largest naval battles of World War I, and it saw the British Grand Fleet emerge victorious against the German High Seas Fleet. The battle was significant because it prevented the German Navy from challenging British supremacy at sea.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of the 5 biggest WW1 sea battles. These battles played a significant role in shaping the course of history, and they had a lasting impact on naval warfare.
