Intro
Stay fit and informed with the Army Physical Training Regulation guide. Learn about the latest APFT standards, Army fitness goals, and exercise protocols. Understand the importance of physical readiness, injury prevention, and performance tracking. Boost your military career with a comprehensive understanding of Army physical training requirements and protocols.
The United States Army Physical Fitness Training Program is a comprehensive and structured approach to physical training, designed to improve the overall fitness and combat readiness of soldiers. The Army Physical Training Regulation, also known as FM 7-22, provides the framework for this program, outlining the principles, methods, and standards for physical training in the Army.
The importance of physical fitness in the Army cannot be overstated. Soldiers must be physically fit to perform their duties effectively, whether in combat or in support roles. Physical fitness is a critical component of a soldier's overall readiness, and it is essential for building and maintaining the strength, endurance, and agility needed to perform tasks that are physically demanding.
The Army Physical Training Regulation is based on the most up-to-date scientific research and evidence-based practices, and it is designed to be flexible and adaptable to meet the diverse needs of soldiers. The regulation provides guidance on the development of physical training programs, including the types of exercises and activities that should be included, as well as the frequency and duration of training.
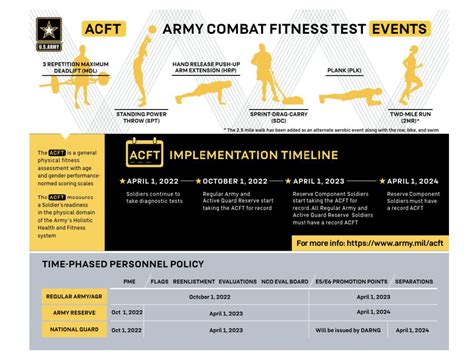
The regulation also outlines the standards for physical fitness testing, including the Army Physical Fitness Test (APFT) and the Body Fat Percentage (BF%) measurement. The APFT is a three-event test that measures a soldier's muscular endurance, cardiovascular endurance, and flexibility. The test consists of push-ups, sit-ups, and a 2-mile run. The BF% measurement is used to assess a soldier's body fat percentage, which is an important indicator of overall health and fitness.
In addition to providing guidance on physical training and testing, the Army Physical Training Regulation also emphasizes the importance of injury prevention and management. The regulation provides guidance on the prevention and treatment of injuries, including the use of physical therapy and rehabilitation programs.
The Army Physical Training Regulation is organized into several chapters, each of which addresses a specific aspect of physical training. The chapters include:
- Chapter 1: Introduction to the Army Physical Fitness Training Program
- Chapter 2: Principles of Physical Training
- Chapter 3: Physical Training Programs
- Chapter 4: Physical Fitness Testing
- Chapter 5: Injury Prevention and Management
- Chapter 6: Physical Training for Special Populations
Each chapter provides detailed guidance on the specific topic, including examples and illustrations to help clarify the concepts.
Principles of Physical Training
The Army Physical Training Regulation is based on several key principles, including:
- Progressive Overload: The principle of progressive overload states that the body adapts to physical stress by becoming stronger and more resilient. To achieve progressive overload, soldiers must gradually increase the intensity of their physical training over time.
- Specificity: The principle of specificity states that physical training should be specific to the task or activity being performed. For example, soldiers who need to perform tasks that require strength and power should engage in strength training exercises.
- Overload: The principle of overload states that physical training should be challenging enough to cause the body to adapt. Soldiers should engage in physical training that pushes them beyond their comfort zone.
- Recovery: The principle of recovery states that rest and recovery are essential for physical adaptation. Soldiers should allow time for rest and recovery between physical training sessions.

Physical Training Programs
The Army Physical Training Regulation provides guidance on the development of physical training programs, including the types of exercises and activities that should be included, as well as the frequency and duration of training. The regulation emphasizes the importance of incorporating a variety of exercises and activities into physical training programs, including:
- Strength Training: Strength training exercises, such as weightlifting and resistance band exercises, are essential for building muscular strength and endurance.
- Cardiovascular Endurance Training: Cardiovascular endurance training, such as running and cycling, is essential for improving cardiovascular health and endurance.
- Flexibility Training: Flexibility training, such as stretching and yoga, is essential for improving flexibility and range of motion.
- Agility Training: Agility training, such as obstacle courses and shuttle runs, is essential for improving speed, agility, and quickness.
The regulation also provides guidance on the frequency and duration of physical training, including the use of periodized training programs. Periodized training programs involve varying the intensity and volume of physical training over time to avoid plateaus and prevent overtraining.
Physical Fitness Testing
The Army Physical Training Regulation outlines the standards for physical fitness testing, including the APFT and the BF% measurement. The APFT is a three-event test that measures a soldier's muscular endurance, cardiovascular endurance, and flexibility. The test consists of push-ups, sit-ups, and a 2-mile run. The BF% measurement is used to assess a soldier's body fat percentage, which is an important indicator of overall health and fitness.

Injury Prevention and Management
The Army Physical Training Regulation emphasizes the importance of injury prevention and management. The regulation provides guidance on the prevention and treatment of injuries, including the use of physical therapy and rehabilitation programs.
The regulation also provides guidance on the use of injury prevention strategies, including:
- Warm-up and Cool-down: Warm-up and cool-down exercises, such as stretching and light cardio, are essential for preventing injuries.
- Proper Technique: Proper technique is essential for preventing injuries, particularly when performing exercises that involve heavy weights or high-impact movements.
- Progressive Overload: Progressive overload is essential for preventing plateaus and preventing overtraining, which can lead to injury.
Physical Training for Special Populations
The Army Physical Training Regulation provides guidance on physical training for special populations, including:
- Pregnant Soldiers: Pregnant soldiers require specialized physical training programs that take into account their physical limitations and health needs.
- Injured Soldiers: Injured soldiers require specialized physical training programs that take into account their physical limitations and health needs.
- Soldiers with Disabilities: Soldiers with disabilities require specialized physical training programs that take into account their physical limitations and health needs.
The regulation provides guidance on the development of physical training programs for these special populations, including the use of modified exercises and activities.

Gallery of Army Physical Training Regulation
Army Physical Training Regulation Image Gallery









What is the Army Physical Training Regulation?
+The Army Physical Training Regulation is a comprehensive guide to physical training in the Army, outlining the principles, methods, and standards for physical training.
What are the principles of physical training?
+The principles of physical training include progressive overload, specificity, overload, and recovery.
What is the Army Physical Fitness Test?
+The Army Physical Fitness Test is a three-event test that measures a soldier's muscular endurance, cardiovascular endurance, and flexibility.
