Intro
Explore the intricacies of a jet engines internal workings with a detailed cross-section breakdown. Discover the 10 essential components, including the compressor, combustion chamber, and turbine, and learn how they work together to generate thrust. Uncover the engineering marvels behind modern aviation and gain a deeper understanding of jet engine design and functionality.
The jet engine is a marvel of modern engineering, providing the power and efficiency needed to propel aircraft through the skies. At its core, a jet engine is a complex piece of machinery that relies on a combination of mechanical and aerodynamic components to generate thrust. By examining a cross-section of a jet engine, we can gain a deeper understanding of the various components that work together to make flight possible.
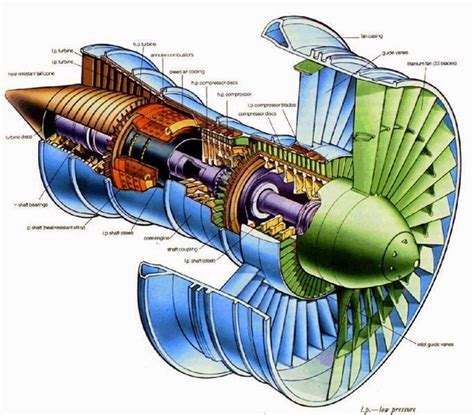
What is a Jet Engine?
Before diving into the components of a jet engine, it's essential to understand the basic principles of how a jet engine works. In simple terms, a jet engine is a type of internal combustion engine that uses the principles of jet propulsion to generate thrust. This is achieved by drawing in air, mixing it with fuel, and then igniting the mixture to produce a high-speed exhaust gas. This exhaust gas is then expelled out of the back of the engine, producing a forward force that propels the aircraft through the air.
Components of a Jet Engine Cross Section
A typical jet engine consists of several key components, each with its own unique function and characteristics. Here are the 10 main components of a jet engine cross-section:
1. Inlet
The inlet is the entrance point of the jet engine, where air is drawn into the engine. The inlet is typically designed to be as large as possible to allow for maximum airflow, while also being shaped to minimize drag.

2. Compressor
The compressor is responsible for compressing the air drawn into the engine, raising its temperature and pressure. This process involves a series of spinning blades that push the air through a narrowing passage, causing its pressure and temperature to increase.

3. Combustion Chamber
The combustion chamber, also known as the combustion can or combustion liner, is where the compressed air is mixed with fuel and ignited. This produces a high-pressure and high-temperature gas that expands rapidly, driving the engine's turbines.

4. Turbine
The turbine is a critical component of the jet engine, responsible for extracting energy from the high-pressure and high-temperature gas produced in the combustion chamber. This energy is then used to drive the compressor and other engine components.
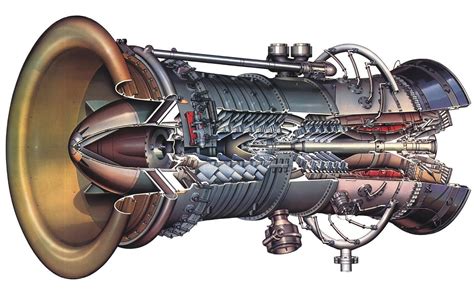
5. Nozzle
The nozzle is the exhaust component of the jet engine, where the high-pressure and high-temperature gas is expelled out of the back of the engine. The nozzle is designed to maximize the exhaust velocity, producing a high-speed jet of gas that generates thrust.

6. Fan
The fan is a large, spinning component located at the front of the engine. Its primary function is to draw in a large volume of air, which is then accelerated by the engine's compressor and turbine.
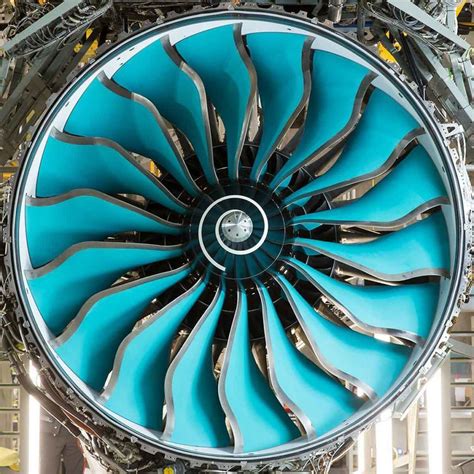

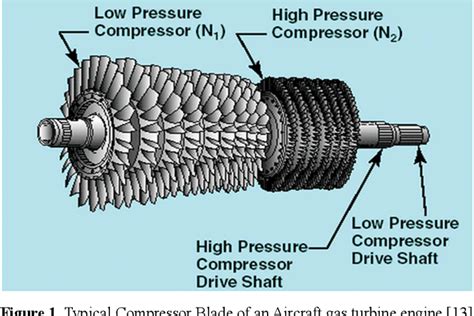
7. Low-Pressure Compressor
The low-pressure compressor is the first stage of the compressor, responsible for compressing the air drawn into the engine. This component is typically driven by the turbine and is designed to provide a high volume of air at a relatively low pressure.
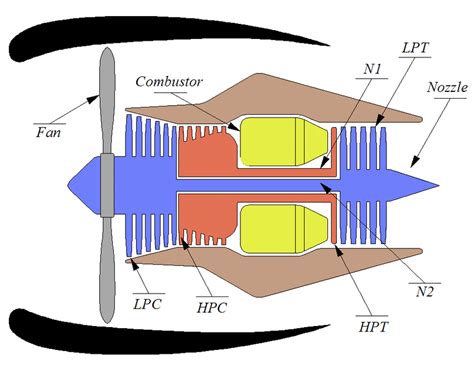
8. High-Pressure Compressor
The high-pressure compressor is the second stage of the compressor, responsible for further compressing the air. This component is also driven by the turbine and is designed to provide a high-pressure air stream that is mixed with fuel in the combustion chamber.
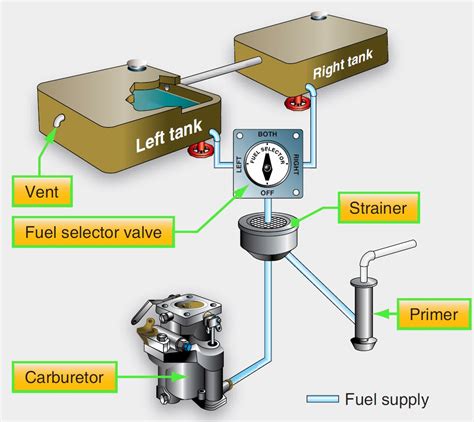
9. Fuel System
The fuel system is responsible for delivering fuel to the combustion chamber, where it is mixed with compressed air and ignited. This component typically consists of a fuel tank, pumps, and fuel lines.
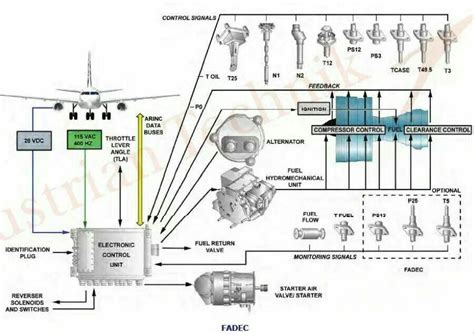
10. Engine Control System
The engine control system is responsible for monitoring and controlling the engine's performance, including parameters such as temperature, pressure, and fuel flow. This component typically consists of sensors, actuators, and a control computer.
Gallery of Jet Engine Components
Jet Engine Components Image Gallery










FAQs
What is the main function of a jet engine?
+The main function of a jet engine is to generate thrust by accelerating a large mass of air rearward, producing a forward force that propels the aircraft through the air.
What are the main components of a jet engine?
+The main components of a jet engine include the inlet, compressor, combustion chamber, turbine, nozzle, fan, low-pressure compressor, high-pressure compressor, fuel system, and engine control system.
How does a jet engine produce thrust?
+A jet engine produces thrust by accelerating a large mass of air rearward, producing a forward force that propels the aircraft through the air. This is achieved by drawing in air, mixing it with fuel, and then igniting the mixture to produce a high-pressure and high-temperature gas that expands rapidly, driving the engine's turbines.
By understanding the components of a jet engine cross-section, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and sophistication of modern aircraft engines. Whether you're an aviation enthusiast or simply interested in learning more about the technology that powers flight, this article has provided a comprehensive overview of the key components that make up a jet engine.
