Intro
Discover the secret to efficient engine performance with the weight to thrust ratio explained simply. Learn how this crucial metric affects aircraft and spacecraft propulsion, fuel efficiency, and overall design. Understand the relationship between weight, thrust, and power-to-weight ratio for optimal performance and range.
Weight to thrust ratio is a crucial concept in aerospace engineering, particularly in the design and development of aircraft, rockets, and spacecraft. It's a measure of an engine's efficiency in generating thrust relative to its weight. In this article, we'll break down the weight to thrust ratio in simple terms, exploring its significance, benefits, and real-world applications.
What is Weight to Thrust Ratio?
Weight to thrust ratio, also known as thrust-to-weight ratio (TWR), is a dimensionless quantity that represents the ratio of an engine's thrust output to its weight. It's calculated by dividing the thrust produced by the engine (in pounds or Newtons) by its weight (in pounds or kilograms). A higher TWR indicates that an engine can produce more thrust relative to its weight, making it more efficient.
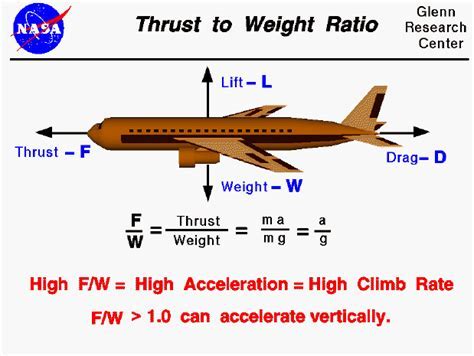
Importance of Weight to Thrust Ratio
The weight to thrust ratio is vital in aerospace engineering because it directly affects the performance and efficiency of an aircraft or spacecraft. A high TWR enables an aircraft to:
- Accelerate faster: With more thrust relative to its weight, an aircraft can accelerate faster, making it more agile and responsive.
- Climb steeper: A higher TWR allows an aircraft to climb steeper, which is essential for military aircraft, spacecraft, and rockets.
- Achieve higher speeds: By producing more thrust relative to its weight, an aircraft can reach higher speeds, making it more efficient for long-range flights.
- Consume less fuel: A more efficient engine with a higher TWR can reduce fuel consumption, leading to lower operating costs and extended range.
Benefits of High Weight to Thrust Ratio
A high weight to thrust ratio offers several benefits, including:
- Improved performance: Higher TWR enables aircraft to perform better, with faster acceleration, steeper climbs, and higher speeds.
- Increased efficiency: More efficient engines reduce fuel consumption, leading to lower operating costs and extended range.
- Enhanced safety: With more thrust relative to its weight, an aircraft can recover faster from stalls or engine failures, improving overall safety.
Real-World Applications
The weight to thrust ratio is crucial in various aerospace applications, including:
- Aircraft design: A high TWR is essential for military aircraft, which require rapid acceleration and steep climbs.
- Spacecraft propulsion: A high TWR is critical for spacecraft, which need to escape Earth's gravity and travel vast distances.
- Rocket design: A high TWR is necessary for rockets, which must produce enormous thrust to achieve orbit or escape Earth's atmosphere.
Calculating Weight to Thrust Ratio
To calculate the weight to thrust ratio, you need to know the engine's thrust output and weight. The formula is:
TWR = Thrust (in pounds or Newtons) / Weight (in pounds or kilograms)
For example, if an engine produces 10,000 pounds of thrust and weighs 2,000 pounds, its TWR would be:
TWR = 10,000 pounds / 2,000 pounds = 5
This means the engine produces 5 pounds of thrust for every pound of weight.
Factors Affecting Weight to Thrust Ratio
Several factors can affect an engine's weight to thrust ratio, including:
- Engine design: The design of the engine, including its configuration, materials, and cooling systems, can impact its TWR.
- Fuel type: The type of fuel used can affect the engine's thrust output and weight, influencing its TWR.
- Operating conditions: Environmental factors, such as air pressure and temperature, can impact an engine's TWR.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the weight to thrust ratio is a critical concept in aerospace engineering, directly affecting the performance and efficiency of aircraft, rockets, and spacecraft. A high TWR enables aircraft to accelerate faster, climb steeper, and achieve higher speeds, while also reducing fuel consumption and improving safety. By understanding the weight to thrust ratio, engineers can design more efficient engines and improve the overall performance of aerospace vehicles.
Weight to Thrust Ratio Image Gallery






What is the weight to thrust ratio?
+The weight to thrust ratio is a dimensionless quantity that represents the ratio of an engine's thrust output to its weight.
Why is the weight to thrust ratio important in aerospace engineering?
+The weight to thrust ratio is crucial in aerospace engineering because it directly affects the performance and efficiency of aircraft, rockets, and spacecraft.
How is the weight to thrust ratio calculated?
+The weight to thrust ratio is calculated by dividing the engine's thrust output by its weight.
