Intro
Discover the role and responsibilities of the National Guard, a reserve component of the US Armed Forces. Learn about its history, mission, and dual state-federal mission, including homeland defense, disaster response, and overseas deployments. Understand the differences between the National Guard and active duty military, and explore the benefits of serving.
The National Guard is a unique element of the United States Armed Forces that serves both state and federal roles. It is a reserve component of the US Army and Air Force, consisting of citizen-soldiers who train part-time to be ready to respond to state and federal emergencies. The National Guard has a long history, dating back to the early days of the American colonies, and has played a significant role in shaping the country's military and civic landscape.

The National Guard is made up of approximately 450,000 soldiers and airmen who serve in the 50 states, three territories, and the District of Columbia. While they are trained and equipped to perform a wide range of military tasks, their primary responsibility is to support state and local authorities during emergencies and disasters.
History of the National Guard
The National Guard has its roots in the colonial era, when local militias were formed to defend against external threats and maintain order within the colonies. After the American Revolution, the militias continued to serve as a vital part of the country's defense system. In 1824, the Militia Act established the framework for the modern National Guard, which was later formalized in 1903 with the passage of the Dick Act.

Throughout its history, the National Guard has played a significant role in many major conflicts, including World War I and II, the Korean War, and the Vietnam War. In recent years, the National Guard has been involved in numerous deployments to the Middle East and other parts of the world, as well as providing support for domestic emergencies and disasters.
Organization and Structure
The National Guard is organized into two main components: the Army National Guard (ARNG) and the Air National Guard (ANG). Each state has its own National Guard organization, with a governor serving as the commander-in-chief. The National Guard is led by the Chief of the National Guard Bureau, who is responsible for overseeing the overall strategy and direction of the organization.
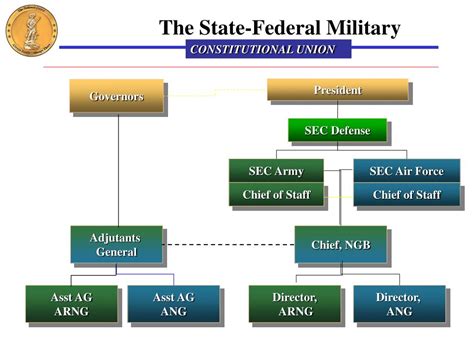
The National Guard is structured into several different units, including infantry, artillery, engineering, and aviation units. These units are trained and equipped to perform a wide range of military tasks, from combat operations to humanitarian assistance and disaster relief.
Roles and Responsibilities
The National Guard has several key roles and responsibilities, including:
- State Emergency Response: The National Guard is responsible for supporting state and local authorities during emergencies and disasters, such as hurricanes, floods, and wildfires.
- Federal Military Operations: The National Guard can be called upon to support federal military operations, both at home and abroad.
- Community Support: The National Guard often provides support to local communities, including participating in parades, fairs, and other civic events.

Benefits of Serving in the National Guard
Serving in the National Guard offers a range of benefits, including:
- Education Benefits: The National Guard offers education benefits, including tuition assistance and the GI Bill.
- Career Opportunities: The National Guard offers a wide range of career opportunities, both in the military and in civilian life.
- Leadership Development: The National Guard provides opportunities for leadership development and training.
- Camaraderie: The National Guard offers a sense of camaraderie and esprit de corps, as well as a chance to serve with fellow citizen-soldiers.

Challenges Facing the National Guard
The National Guard faces a range of challenges, including:
- Recruitment and Retention: The National Guard often struggles with recruitment and retention, particularly in certain specialties and regions.
- Equipment and Resources: The National Guard often has limited access to equipment and resources, particularly compared to the active duty military.
- Deployments: The National Guard is often called upon to deploy overseas, which can be challenging for both soldiers and their families.

Conclusion
The National Guard is a vital component of the US Armed Forces, serving both state and federal roles. With its rich history, diverse structure, and wide range of responsibilities, the National Guard offers a unique and rewarding opportunity for citizen-soldiers to serve their country and their communities. While the National Guard faces a range of challenges, its importance and value to the nation cannot be overstated.
National Guard Image Gallery










What is the National Guard?
+The National Guard is a reserve component of the US Armed Forces that serves both state and federal roles. It is made up of citizen-soldiers who train part-time to be ready to respond to state and federal emergencies.
What is the history of the National Guard?
+The National Guard has its roots in the colonial era, when local militias were formed to defend against external threats and maintain order within the colonies. After the American Revolution, the militias continued to serve as a vital part of the country's defense system.
What are the benefits of serving in the National Guard?
+Serving in the National Guard offers a range of benefits, including education benefits, career opportunities, leadership development, and camaraderie.
