Intro
Discover the flexibility and fulfillment of serving in the Navy Reserve. Learn about 5 ways to serve, including part-time and full-time options, and how to balance military service with civilian life. Explore opportunities for career advancement, education assistance, and camaraderie, all while supporting national defense as a Navy Reserve Sailor.
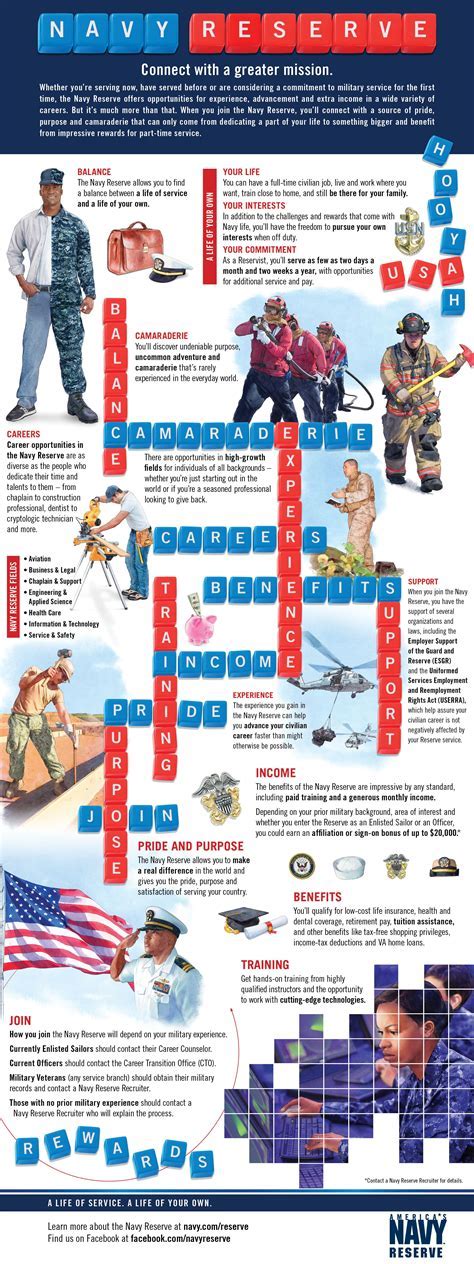
Serving in the Navy Reserve can be a rewarding and challenging experience, offering individuals the opportunity to serve their country while also pursuing their civilian careers and personal goals. The Navy Reserve provides a unique blend of flexibility and service, allowing Reservists to serve on a part-time basis while still contributing to the nation's defense. If you're considering serving in the Navy Reserve, here are five ways to serve:
Drilling Reservist

As a Drilling Reservist, you will serve one weekend a month, known as a drill weekend, and two weeks a year, known as annual training (AT). During this time, you will perform duties similar to those of active-duty personnel, including training, maintenance, and operations. Drilling Reservists are an essential part of the Navy Reserve, providing critical support to the active-duty Navy and helping to maintain the readiness of the fleet.
Full-Time Support (FTS) Personnel

Full-Time Support (FTS) personnel are Navy Reservists who serve on active duty in support of the Navy Reserve. They work full-time, Monday through Friday, and are responsible for a variety of tasks, including training, administration, and maintenance. FTS personnel play a critical role in supporting the Navy Reserve, helping to ensure that units are trained and equipped to deploy when needed.
Individual Augmentee (IA)

As an Individual Augmentee (IA), you will be assigned to a specific unit or organization for a specific period, usually 12-18 months. During this time, you will perform duties similar to those of active-duty personnel, including training, operations, and maintenance. IAs are an essential part of the Navy Reserve, providing critical support to the active-duty Navy and helping to maintain the readiness of the fleet.
Active Duty for Special Work (ADSW)

Active Duty for Special Work (ADSW) is a program that allows Navy Reservists to serve on active duty for a specific period, usually 12-18 months. During this time, you will perform duties similar to those of active-duty personnel, including training, operations, and maintenance. ADSW personnel are an essential part of the Navy Reserve, providing critical support to the active-duty Navy and helping to maintain the readiness of the fleet.
Annual Training (AT)

Annual Training (AT) is a two-week period during which Navy Reservists report for duty to perform training, maintenance, and operations. AT is an essential part of the Navy Reserve, providing critical training and support to the active-duty Navy and helping to maintain the readiness of the fleet. During AT, you will have the opportunity to work alongside active-duty personnel, receive training, and participate in operations and maintenance activities.
Benefits of Serving in the Navy Reserve
Serving in the Navy Reserve offers a range of benefits, including:
- Education Benefits: The Navy Reserve offers a range of education benefits, including the Montgomery GI Bill Selected Reserve (MGIB-SR) and the Navy Reserve Tuition Assistance Program.
- Career Advancement: Serving in the Navy Reserve can provide valuable career experience and training, helping to advance your civilian career.
- Leadership Opportunities: The Navy Reserve offers a range of leadership opportunities, helping to develop your leadership and management skills.
- Camaraderie: Serving in the Navy Reserve provides the opportunity to build lasting relationships with fellow Reservists and active-duty personnel.
- Sense of Purpose: Serving in the Navy Reserve provides a sense of purpose and fulfillment, knowing that you are contributing to the nation's defense.
How to Join the Navy Reserve
If you're interested in joining the Navy Reserve, here are the steps to follow:
- Meet the Eligibility Requirements: You must meet the eligibility requirements, including age, citizenship, and education requirements.
- Choose a Rating: You must choose a rating, or job specialty, that aligns with your skills and interests.
- Complete the Application Process: You must complete the application process, including submitting your application and supporting documentation.
- Take the ASVAB Test: You must take the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test to determine your eligibility for certain ratings.
- Complete Boot Camp: You must complete boot camp, also known as Basic Training, to prepare for service in the Navy Reserve.
Gallery of Navy Reserve Images
Navy Reserve Image Gallery









What are the eligibility requirements for joining the Navy Reserve?
+The eligibility requirements for joining the Navy Reserve include age, citizenship, education, and physical fitness requirements.
What is the difference between a Drilling Reservist and a Full-Time Support (FTS) personnel?
+A Drilling Reservist serves one weekend a month and two weeks a year, while a Full-Time Support (FTS) personnel serves on active duty in support of the Navy Reserve.
What are the benefits of serving in the Navy Reserve?
+The benefits of serving in the Navy Reserve include education benefits, career advancement opportunities, leadership opportunities, camaraderie, and a sense of purpose.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of the different ways to serve in the Navy Reserve. Whether you're interested in serving as a Drilling Reservist, Full-Time Support (FTS) personnel, Individual Augmentee (IA), or Active Duty for Special Work (ADSW), the Navy Reserve offers a range of opportunities for those looking to serve their country while also pursuing their civilian careers and personal goals.
