Intro
Discover the rich history of the US military establishment. Learn when the US military was founded, its evolution over time, and key milestones that shaped its growth. From the Continental Army to the modern-day armed forces, explore the fascinating story of the US militarys founding and development.
The United States military has a rich and complex history that spans over two centuries. The exact date of its establishment is a matter of debate among historians, as it evolved from a group of colonial militias to a unified national army. However, I can provide you with an overview of the key milestones that led to the creation of the US military as we know it today.
In the early days of American colonization, each state had its own militia, which was a group of citizen-soldiers who were responsible for defending their colony against external threats. These militias played a crucial role in the American Revolutionary War, fighting against the British army and its allies.
After the Revolutionary War, the Continental Congress, which was the governing body of the newly independent United States, recognized the need for a unified national army. On June 3, 1784, the Continental Congress passed a resolution that established the United States Army as a permanent military force. However, this early army was small and had limited powers.
The US military as we know it today began to take shape during the late 18th and early 19th centuries. In 1796, the US Congress passed the "Act for the Establishment of a Militia," which created a system of militias that were organized and trained by the federal government. This act also established the Office of the Adjutant General, which was responsible for overseeing the militias.
The War of 1812 marked a significant turning point in the development of the US military. The war highlighted the need for a more professional and better-trained army, and it led to the establishment of the United States Military Academy at West Point in 1802. The academy, which was founded by President Thomas Jefferson, became a hub for military education and training, and it played a crucial role in shaping the US military into a modern, professional force.
The Mexican-American War (1846-1848) and the American Civil War (1861-1865) further solidified the US military's role in American society. The Civil War, in particular, saw the emergence of the US military as a powerful and modern force, with the establishment of the first military draft and the creation of the Union and Confederate armies.
In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the US military underwent significant reforms and modernization efforts. The Spanish-American War (1898) marked the beginning of the US military's global expansion, and World War I (1914-1918) saw the US military emerge as a major world power.
Today, the US military is one of the most powerful and technologically advanced forces in the world, with a global presence and a wide range of responsibilities, from defending American interests to providing humanitarian aid and disaster relief.
Key Milestones in the Establishment of the US Military
- 1775: The Continental Congress establishes the Continental Army, which fights against the British army in the American Revolutionary War.
- 1784: The Continental Congress passes a resolution establishing the United States Army as a permanent military force.
- 1796: The US Congress passes the "Act for the Establishment of a Militia," which creates a system of militias that are organized and trained by the federal government.
- 1802: The United States Military Academy at West Point is founded by President Thomas Jefferson.
- 1812: The War of 1812 highlights the need for a more professional and better-trained army.
- 1846-1848: The Mexican-American War sees the emergence of the US military as a major force in North America.
- 1861-1865: The American Civil War solidifies the US military's role in American society and leads to the establishment of the first military draft.
- 1898: The Spanish-American War marks the beginning of the US military's global expansion.
- 1914-1918: World War I sees the US military emerge as a major world power.

Structure of the US Military
The US military is composed of five branches: the United States Army, the United States Navy, the United States Air Force, the United States Marine Corps, and the United States Coast Guard. Each branch has its own unique mission, responsibilities, and culture.
- United States Army: The US Army is the largest branch of the US military, with approximately 475,000 active-duty soldiers. Its primary mission is to protect the American people and the nation's interests through land-based military operations.
- United States Navy: The US Navy is the second-largest branch of the US military, with approximately 330,000 active-duty personnel. Its primary mission is to protect American interests through naval operations, including sea-based defense and power projection.
- United States Air Force: The US Air Force is the youngest branch of the US military, established in 1947. It has approximately 329,000 active-duty personnel and its primary mission is to protect American interests through air-based military operations.
- United States Marine Corps: The US Marine Corps is the smallest branch of the US military, with approximately 186,000 active-duty personnel. Its primary mission is to provide power projection from the sea, using its unique blend of air, land, and sea capabilities.
- United States Coast Guard: The US Coast Guard is a unique branch of the US military that operates under the Department of Homeland Security during peacetime. Its primary mission is to protect American interests and enforce maritime law, including search and rescue, maritime law enforcement, and marine safety.

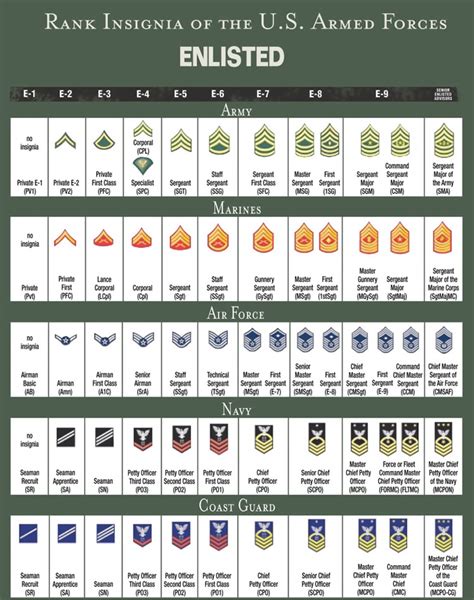
US Military Ranks and Insignia
The US military uses a system of ranks and insignia to identify an individual's position and level of authority within their branch. Each branch has its own unique system of ranks and insignia, but they all follow a similar pattern.
- Enlisted Ranks: Enlisted personnel are the backbone of the US military, making up approximately 85% of all military personnel. Enlisted ranks range from Private (E-1) to Command Sergeant Major (E-9) in the Army, and from Seaman Recruit (E-1) to Master Chief Petty Officer (E-9) in the Navy.
- Warrant Officer Ranks: Warrant officers are technical experts in their field and serve as advisors to commanders. Warrant officer ranks range from Warrant Officer 1 (W-1) to Chief Warrant Officer 5 (W-5) in the Army, and from Warrant Officer 1 (W-1) to Chief Warrant Officer 4 (W-4) in the Navy.
- Officer Ranks: Officers are leaders in the US military, responsible for making strategic decisions and commanding units. Officer ranks range from Second Lieutenant (O-1) to General (O-10) in the Army, and from Ensign (O-1) to Admiral (O-10) in the Navy.
US Military Equipment and Technology
The US military is equipped with some of the most advanced technology and equipment in the world. From fighter jets to tanks, and from submarines to aircraft carriers, the US military has a wide range of equipment at its disposal.
- Fighter Jets: The US military operates a range of fighter jets, including the F-15 Eagle, the F-16 Fighting Falcon, and the F-22 Raptor.
- Tanks: The US military operates a range of tanks, including the M1 Abrams and the M2 Bradley.
- Submarines: The US military operates a range of submarines, including the Los Angeles-class and the Virginia-class.
- Aircraft Carriers: The US military operates a range of aircraft carriers, including the Nimitz-class and the Gerald R. Ford-class.

US Military Bases and Installations
The US military operates a range of bases and installations around the world, from major bases in the United States to smaller installations in remote locations.
- Major Bases: The US military operates a range of major bases in the United States, including Fort Bragg in North Carolina, Fort Hood in Texas, and Camp Pendleton in California.
- Overseas Bases: The US military operates a range of bases overseas, including Ramstein Air Base in Germany, Yokosuka Naval Base in Japan, and Camp Humphreys in South Korea.

US Military Operations and Missions
The US military is involved in a range of operations and missions around the world, from combat operations in Afghanistan and Iraq to humanitarian aid and disaster relief efforts.
- Combat Operations: The US military is involved in combat operations in a range of countries, including Afghanistan and Iraq.
- Humanitarian Aid: The US military provides humanitarian aid and disaster relief efforts around the world, including in response to natural disasters such as hurricanes and earthquakes.
- Peacekeeping: The US military is involved in peacekeeping operations around the world, including in the Balkans and Africa.

US Military Veterans and Benefits
The US military offers a range of benefits to its veterans, including education benefits, healthcare benefits, and employment benefits.
- Education Benefits: The US military offers education benefits to its veterans, including the GI Bill and the Military Tuition Assistance Program.
- Healthcare Benefits: The US military offers healthcare benefits to its veterans, including medical, dental, and pharmacy benefits.
- Employment Benefits: The US military offers employment benefits to its veterans, including preferential hiring and training programs.

US Military Image Gallery










What is the US military?
+The US military is the armed forces of the United States, consisting of the Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard.
What is the purpose of the US military?
+The purpose of the US military is to protect the American people and the nation's interests through military operations, including defense, deterrence, and humanitarian aid.
How is the US military organized?
+The US military is organized into five branches: the Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard. Each branch has its own unique mission, responsibilities, and culture.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of the US military, its history, structure, equipment, and operations. The US military is a complex and multifaceted institution that plays a critical role in protecting American interests and promoting peace and stability around the world.
