Intro
Uncover the 5 key differences between U-boats and submarines. Learn about their historical roles, design variations, and operational distinctions. From World War-era German U-boats to modern nuclear-powered submarines, discover the unique characteristics that set them apart. Dive into the world of underwater warfare and exploration.
The world of underwater vessels is a fascinating one, with a rich history and a multitude of designs and capabilities. Two of the most well-known types of underwater vessels are the U-boat and the submarine. While they share some similarities, they also have several key differences. In this article, we will explore five of the main differences between U-boats and submarines.
What is a U-Boat?
Before we dive into the differences, let's take a brief look at what a U-boat is. A U-boat is a type of German submarine that was used extensively during World War I and World War II. The term "U-boat" comes from the German word "U-Boot," which means "undersea boat." U-boats were designed for military use, primarily for attacking enemy ships and disrupting supply lines.
What is a Submarine?
A submarine, on the other hand, is a general term that refers to any underwater vessel that operates independently, without the need for a surface support ship. Submarines can be used for a variety of purposes, including military, scientific, and commercial applications.
Difference 1: Origin and History
One of the main differences between U-boats and submarines is their origin and history. U-boats were specifically designed and built by Germany during World War I and World War II, whereas submarines have a longer and more diverse history that spans multiple countries and centuries.
Difference 2: Design and Construction
Another difference between U-boats and submarines is their design and construction. U-boats were typically smaller and more compact than submarines, with a focus on stealth and agility. They were also designed to operate in coastal waters and had a relatively short range. Submarines, on the other hand, can range in size from small, coastal vessels to large, ocean-going ships.

Difference 3: Military vs. Non-Military Use
U-boats were primarily designed for military use, whereas submarines can be used for a variety of purposes, including military, scientific, and commercial applications. While some submarines are designed for military use, others are used for research, exploration, or transportation.
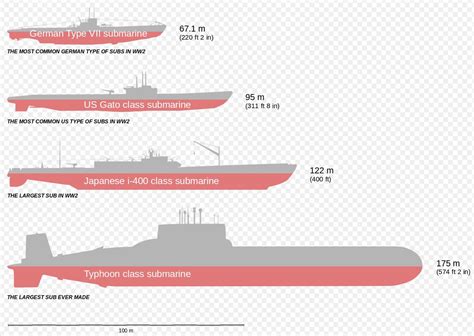
Difference 4: Size and Range
U-boats were generally smaller than submarines, with a typical length of around 60-80 meters. Submarines, on the other hand, can range in size from small, 20-meter vessels to large, 150-meter ships. Submarines also have a longer range than U-boats, with some capable of traveling thousands of miles without surfacing.

Difference 5: Propulsion and Speed
Finally, U-boats and submarines differ in terms of propulsion and speed. U-boats were typically powered by diesel-electric propulsion, which allowed them to operate quietly and efficiently. Submarines, on the other hand, can be powered by a variety of systems, including diesel-electric, nuclear, or air-independent propulsion. Submarines are generally faster than U-boats, with some capable of reaching speeds of over 20 knots.

Gallery of Submarine and U-Boat Images
Submarine and U-Boat Image Gallery










Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between a U-boat and a submarine?
+The main difference between a U-boat and a submarine is their origin and history. U-boats were specifically designed and built by Germany during World War I and World War II, whereas submarines have a longer and more diverse history that spans multiple countries and centuries.
What is the typical size of a U-boat?
+U-boats are generally smaller than submarines, with a typical length of around 60-80 meters.
What is the main purpose of a submarine?
+Submarines can be used for a variety of purposes, including military, scientific, and commercial applications.
What is the difference between diesel-electric propulsion and nuclear propulsion?
+Diesel-electric propulsion uses diesel engines to generate electricity, which is then used to power the submarine's propeller. Nuclear propulsion, on the other hand, uses a nuclear reactor to generate steam, which is then used to power the submarine's propeller.
How fast can a submarine travel?
+Submarines can travel at speeds of up to 20 knots, although some modern submarines can reach speeds of over 25 knots.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, while U-boats and submarines share some similarities, they also have several key differences. From their origin and history to their design and construction, these two types of underwater vessels have distinct characteristics that set them apart. Whether you're interested in military history or simply want to learn more about the world of underwater vessels, understanding the differences between U-boats and submarines is a great place to start.
