Intro
Discover how WW1 revolutionized communication with the creation of the phonetic alphabet. Learn how the wars chaos led to the development of a standardized system, making radio transmissions clearer and safer. Explore the impact on military ops, aviation, and everyday life, and find out how this innovation still influences us today.
The phonetic alphabet, also known as the NATO phonetic alphabet, is a standardized system used to clearly communicate letters and numbers over radio and phone communications. While it may seem like a mundane tool, the phonetic alphabet has a rich history that dates back to World War I. In this article, we will explore five ways in which WW1 created the phonetic alphabet.
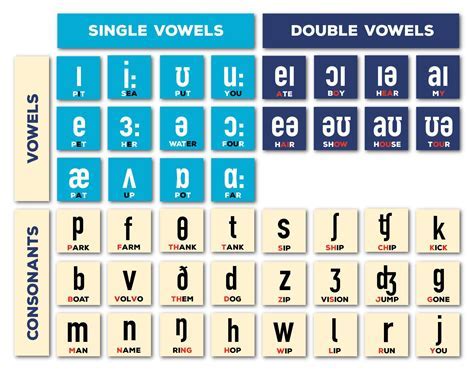
The Chaos of Radio Communications
During WW1, radio communication was still in its infancy. Radio operators relied on Morse code to transmit messages, but this system had its limitations. As the war progressed, the need for clear and concise communication over radio became increasingly important. However, the technology at the time was prone to errors, and the sounds of letters and numbers were often confused.
For example, the letter "B" and "P" sounded similar over radio, and the numbers "5" and "9" could be easily mistaken. To address this issue, the military began to develop a system that would clearly differentiate between letters and numbers.
The Birth of the Phonetic Alphabet
In 1915, the British Royal Navy introduced a phonetic alphabet system to improve communication over radio. This system used distinct words to represent each letter of the alphabet, such as "Able" for the letter "A" and "Baker" for the letter "B". The use of words instead of letters helped to reduce errors and improve communication.

The Development of the A1Z26 System
In 1918, the American Expeditionary Forces (AEF) developed the A1Z26 system, which used a combination of letters and numbers to represent each letter of the alphabet. This system was more complex than the British system but provided a higher level of accuracy.
The A1Z26 system used a combination of letters and numbers to represent each letter of the alphabet, such as "A1" for the letter "A" and "B2" for the letter "B". This system was widely used during WW1 and laid the foundation for the modern phonetic alphabet.
The International Radiotelegraph Convention
In 1927, the International Radiotelegraph Convention was held in Washington, D.C. to standardize radio communication systems. The convention established the International Radiotelegraph Phonetic Alphabet, which was based on the A1Z26 system.
The International Radiotelegraph Phonetic Alphabet used a combination of letters and numbers to represent each letter of the alphabet, such as "A1" for the letter "A" and "B2" for the letter "B". This system was widely adopted by countries around the world and remained in use until the 1950s.

The Modern Phonetic Alphabet
In 1959, the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) developed the modern phonetic alphabet, also known as the NATO phonetic alphabet. This system uses distinct words to represent each letter of the alphabet, such as "Alpha" for the letter "A" and "Bravo" for the letter "B".
The modern phonetic alphabet is widely used today in radio communication, aviation, and maritime industries. It is an essential tool for clear and concise communication, and its development can be attributed to the chaos of radio communications during WW1.
Gallery of WW1 Communication Images
WW1 Communication Image Gallery








What is the phonetic alphabet?
+The phonetic alphabet is a standardized system used to clearly communicate letters and numbers over radio and phone communications.
Why was the phonetic alphabet developed?
+The phonetic alphabet was developed to improve communication over radio during WW1, where the technology at the time was prone to errors.
What is the modern phonetic alphabet?
+The modern phonetic alphabet is the NATO phonetic alphabet, which uses distinct words to represent each letter of the alphabet, such as "Alpha" for the letter "A" and "Bravo" for the letter "B".
In conclusion, the phonetic alphabet has a rich history that dates back to WW1. The chaos of radio communications during the war led to the development of a standardized system for clear and concise communication. Today, the modern phonetic alphabet is widely used in radio communication, aviation, and maritime industries. We hope this article has provided you with a deeper understanding of the phonetic alphabet and its significance in modern communication.
